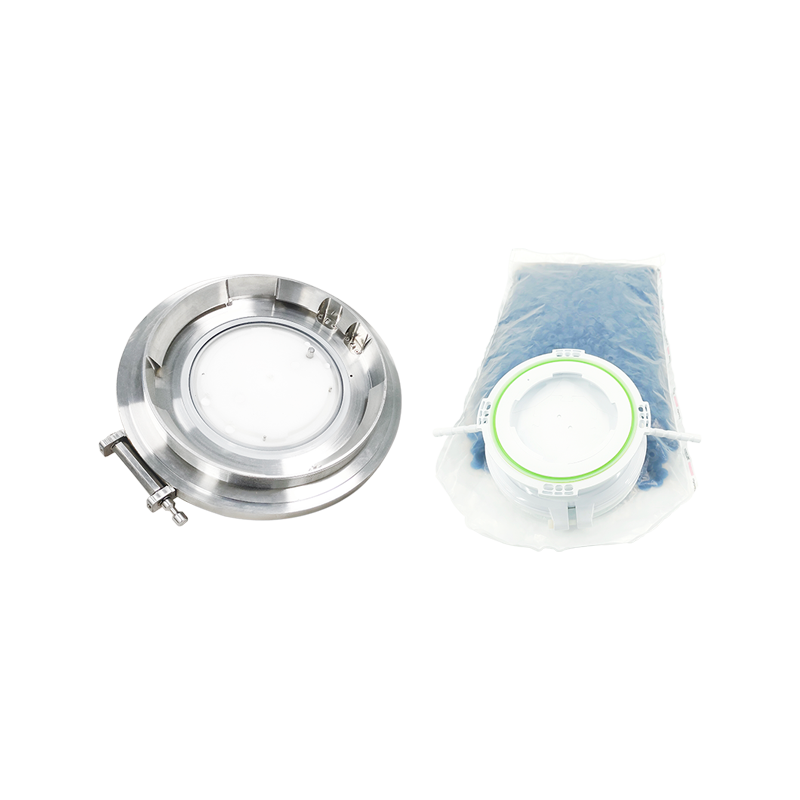
RTP Beta Bags are a critical component of Rapid Transfer Port (RTP) systems widely used in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and high-containment manufacturing environments. Their primary role is to enable the safe, sterile, and contained transfer of materials into and out of isolators or restricted access barrier systems (RABS) without compromising environmental integrity.
When comparing RTP Beta Bags with other containment bags, the differences are not limited to shape or material alone. They extend to connection mechanisms, sterility assurance, regulatory acceptance, and the level of operator protection provided. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right containment solution for critical processes.
Design and Structural Differences
One of the most fundamental differences between RTP Beta Bags and other containment bags lies in their structural design. RTP Beta Bags are specifically engineered to integrate with Beta ports, forming a sealed interface that supports alpha-beta docking operations.
RTP-Specific Docking Interface
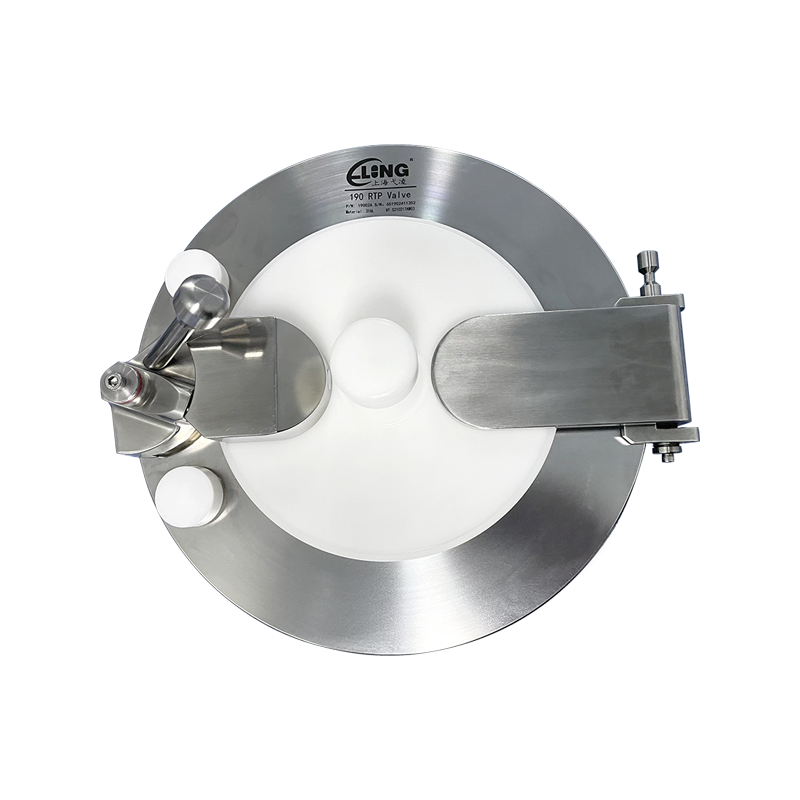
RTP Beta Bags feature a rigid or semi-rigid beta flange designed to mate precisely with an alpha port mounted on an isolator or enclosure. This interface ensures a closed transfer, allowing materials to move without exposing either the internal or external environment. Most conventional containment bags rely on manual opening, tie-offs, or glove handling, which inherently increases contamination risk.
Bag Geometry and Reinforcement
Compared to standard polyethylene or multi-layer containment bags, RTP Beta Bags often incorporate reinforced seams, controlled bag geometry, and engineered stress points. These features help maintain structural integrity during docking, rotation, and undocking operations, which are unique to RTP systems.
Material Composition and Performance
Material selection plays a crucial role in differentiating RTP Beta Bags from other containment bag types. The materials must support sterility, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability while remaining compatible with pharmaceutical cleanroom standards.
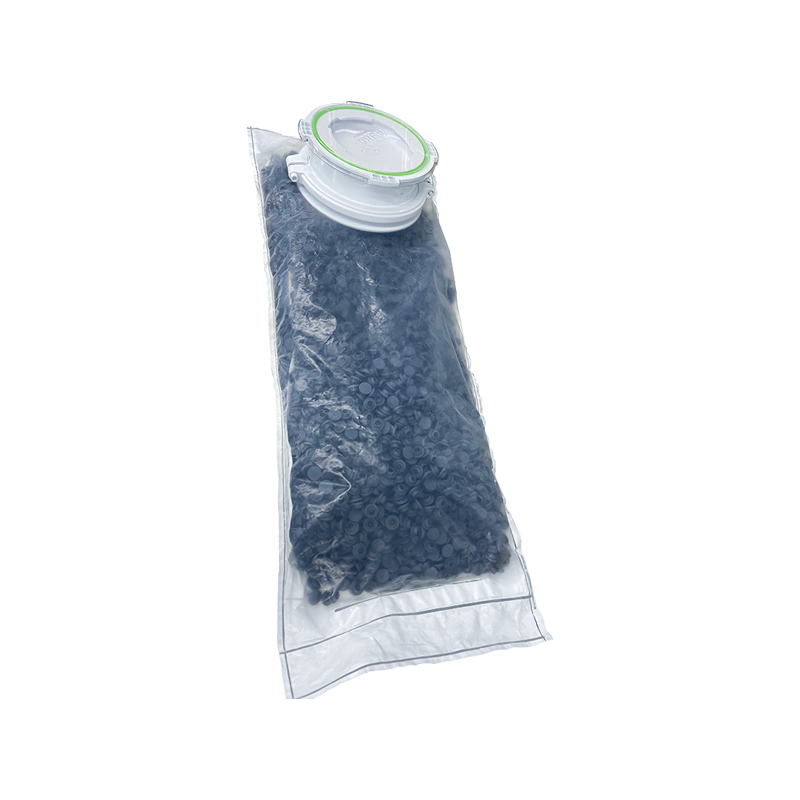

Multi-Layer High-Barrier Films
RTP Beta Bags are typically manufactured using multi-layer films such as PE/EVOH/PE or specialized polymer laminates. These structures offer enhanced barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and microbial ingress. Many generic containment bags prioritize cost over barrier performance and may not provide equivalent protection in long-term or high-risk applications.
Chemical and Decontamination Compatibility
Unlike standard containment bags, RTP Beta Bags are validated for compatibility with vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP), peracetic acid, or other decontamination agents used in isolators. This compatibility ensures that the bag material does not degrade, discolor, or release particulates during routine decontamination cycles.
Sterility Assurance and Contamination Control
Sterility assurance is one of the most significant differentiators between RTP Beta Bags and other containment solutions. RTP systems are designed to support aseptic processing under stringent regulatory requirements.
Pre-Sterilized and Validated Options
RTP Beta Bags are commonly supplied pre-sterilized using gamma irradiation or other validated sterilization methods. Sterility assurance levels (SAL) are documented and traceable, which is essential for GMP-compliant operations. In contrast, many other containment bags are delivered non-sterile and rely on in-house cleaning or secondary packaging.
Closed Transfer vs Open Handling
The closed transfer principle supported by RTP Beta Bags significantly reduces the risk of human intervention and airborne contamination. Other containment bags often require partial opening, cutting, or manual sealing steps, increasing the likelihood of contamination or operator exposure.
Operational Efficiency and Workflow Impact
From an operational perspective, RTP Beta Bags offer workflow advantages that are difficult to replicate with conventional containment bags, particularly in high-throughput or high-risk environments.
- Faster material transfer with minimal manual intervention
- Reduced gowning and degowning requirements for operators
- Lower risk of process interruptions due to contamination events
Traditional containment bags may be suitable for low-risk material handling, but they often introduce inefficiencies when used in aseptic or potent compound manufacturing where strict controls are mandatory.
Application Scope and Industry Use
The intended application is another area where RTP Beta Bags differ significantly from other containment bags. Their design aligns closely with regulated industries and critical manufacturing processes.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech Manufacturing
RTP Beta Bags are extensively used for transferring active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), sterile components, tools, and waste in GMP environments. Other containment bags may lack the documentation, validation support, or performance consistency required for regulatory inspections.
High-Potency and Toxic Material Handling
In high-containment facilities handling cytotoxic or highly potent compounds, RTP Beta Bags provide superior operator protection. The sealed interface minimizes exposure risks compared to conventional bags that depend on manual sealing or double-bagging techniques.
Comparison Table: RTP Beta Bags vs Other Containment Bags
| Feature | RTP Beta Bags | Other Containment Bags |
| Transfer Method | Closed alpha-beta docking | Manual opening or sealing |
| Sterility Assurance | Validated, pre-sterilized | Often non-sterile |
| Decontamination Compatibility | VHP and chemical compatible | Limited or unvalidated |
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Value
While RTP Beta Bags generally have a higher unit cost than standard containment bags, the overall cost of ownership is often lower. Reduced contamination risk, fewer process deviations, and improved operator safety contribute to long-term operational savings.
For facilities operating under strict regulatory oversight, the added cost of RTP Beta Bags is frequently justified by compliance assurance and risk reduction.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Containment Solution
The key differences between RTP Beta Bags and other containment bags center on containment integrity, sterility assurance, and system compatibility. RTP Beta Bags are purpose-built for closed transfer in critical environments, offering advantages that generic containment bags cannot match.
By evaluating process risk, regulatory requirements, and operational workflows, manufacturers can determine whether RTP Beta Bags provide the appropriate level of control and protection for their containment needs.