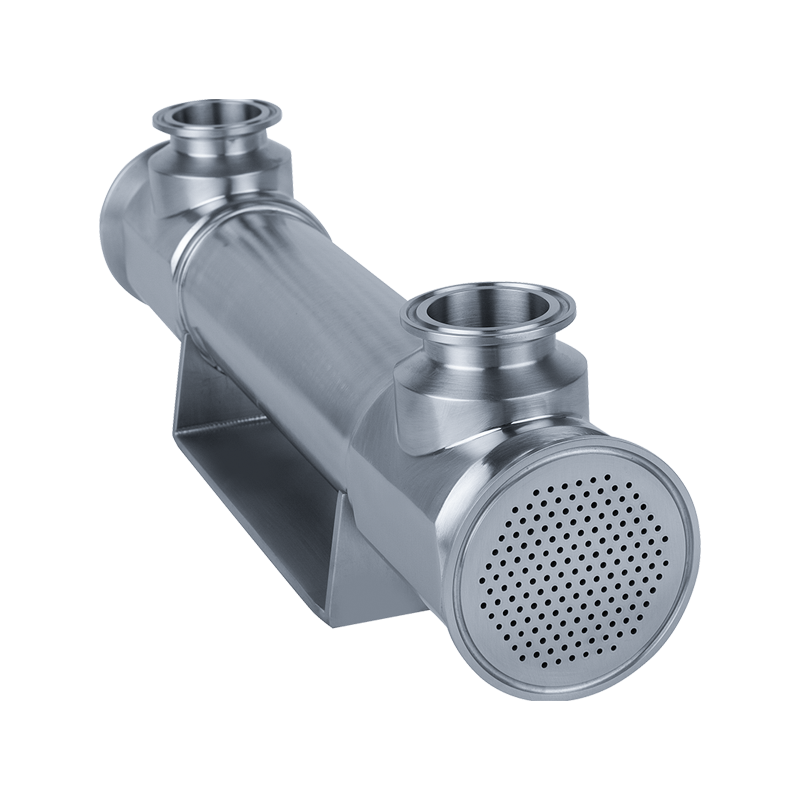
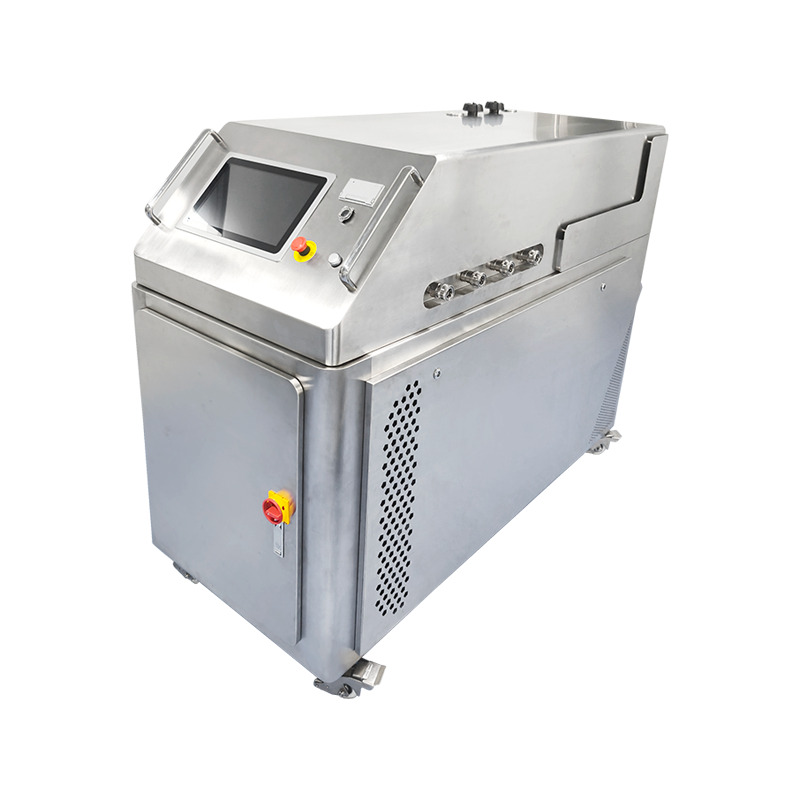
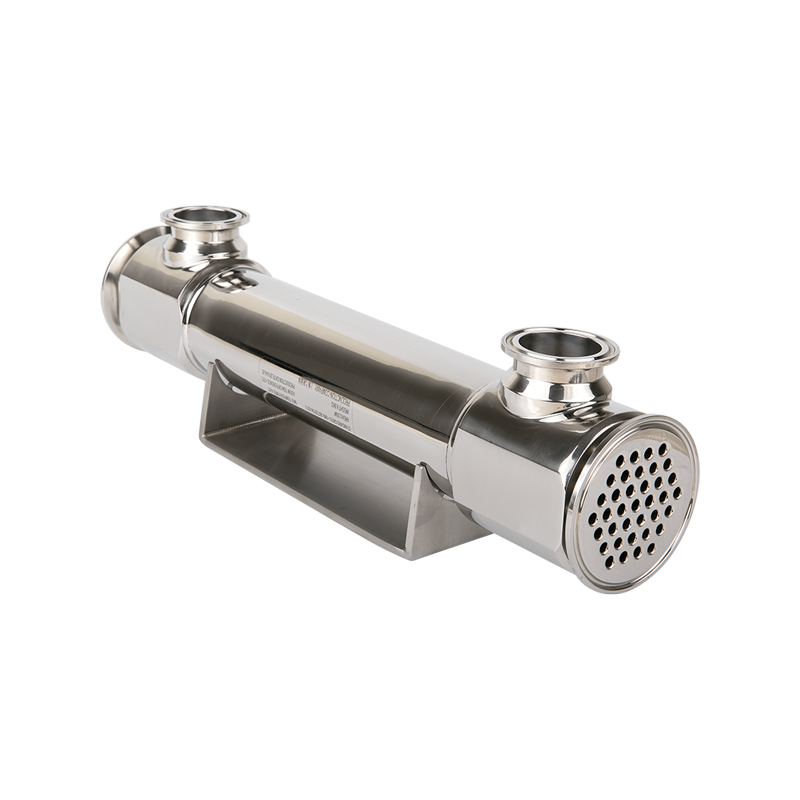
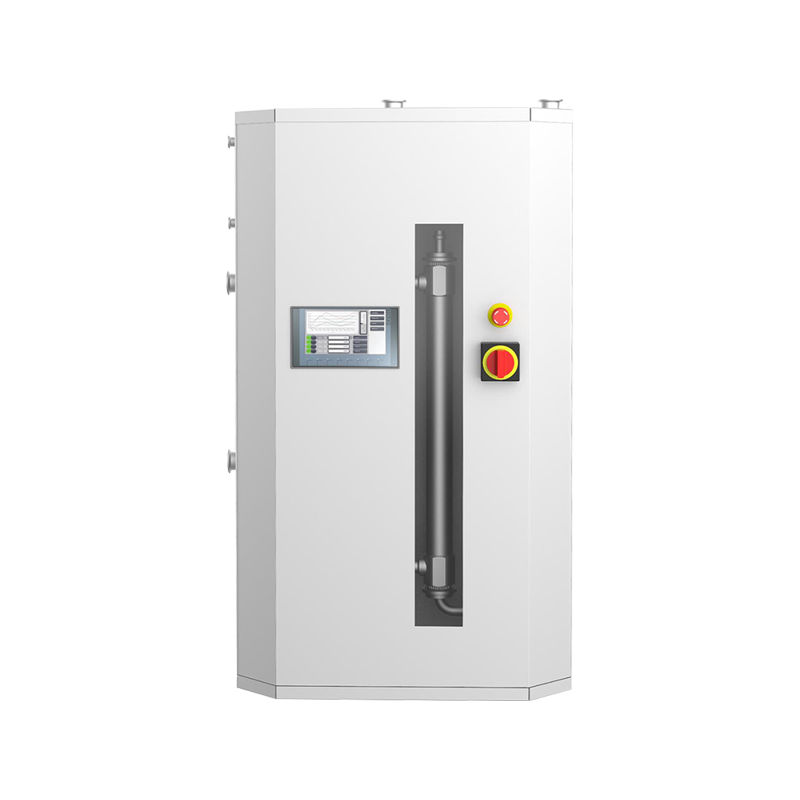
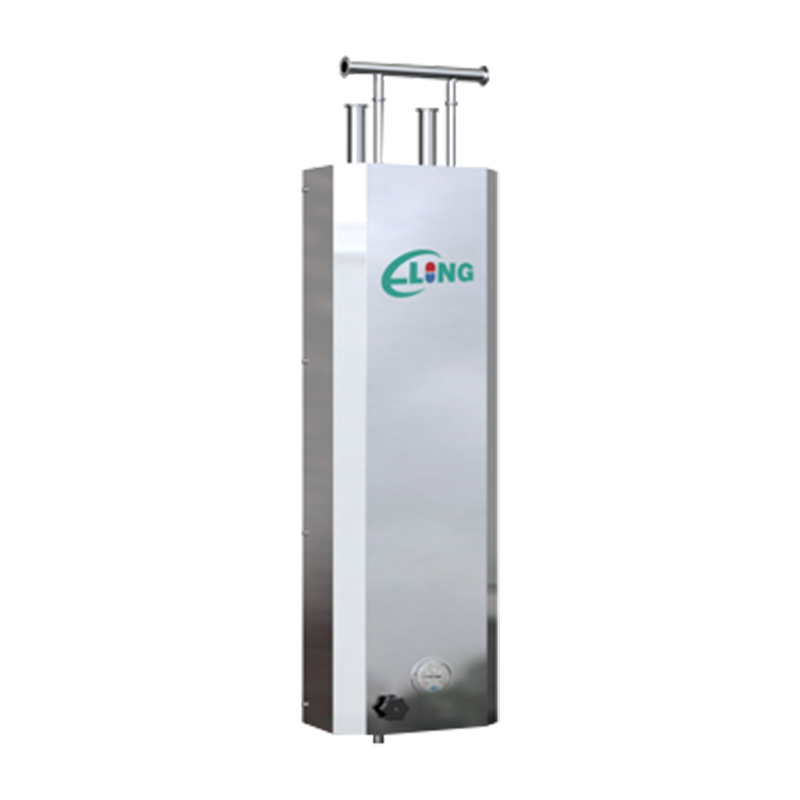
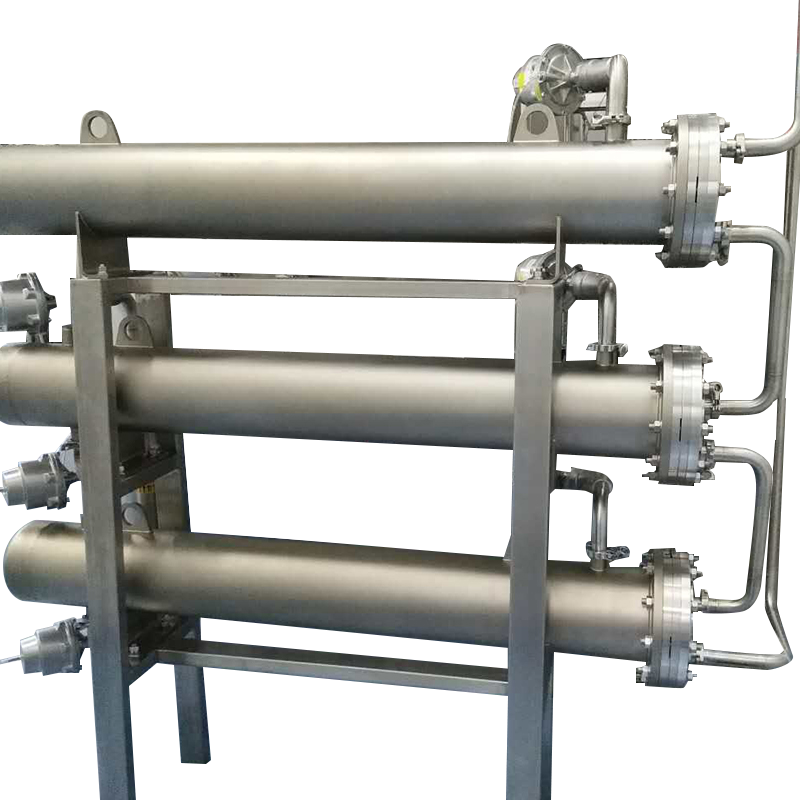
In modern industrial production and energy conversion, heat exchange equipment plays an extremely important role. Among them, shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used in petrochemical, electric power, pharmaceutical, food, HVAC and other fields due to their simple structure, strong adaptability and high heat exchange efficiency. This article will introduce the structural characteristics, working principle, core advantages and typical applications of shell and tube heat exchangers in detail.
During operation, one fluid (such as hot water, steam or high-temperature oil) enters the tube side, and another fluid (such as cooling water or low-temperature liquid) enters the shell side. The hot fluid transfers heat to the cold fluid through the tube wall, thereby realizing efficient transfer of heat energy. This heat exchange method effectively avoids fluid mixing and ensures the independence and safety of the medium.
The core advantages of shell and tube heat exchangers
Strong structure, adaptable to high temperature and high pressure environment
Shell and tube heat exchangers are made of metal materials, have good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, and can operate stably under high temperature, high pressure and even highly corrosive media conditions.
High heat exchange efficiency and large heat transfer area
The tube bundles are tightly arranged and the length can be customized, providing a large heat exchange area. At the same time, the fluid disturbance can be improved through multi-pass design, adding baffles, etc., to enhance the heat exchange effect.
Easy maintenance and long service life
The shell and tube heat exchanger has a simple structure, is easy to disassemble, and is easy to clean and repair. As long as it is maintained regularly, its service life can usually reach more than 10 years, with good economic efficiency.
A variety of structural forms, flexible adaptation to working conditions
Different structural forms can be selected according to the type of medium, pressure level and usage scenario, such as fixed tube sheet type, floating head type, U-tube type, etc., to meet the diverse needs of different industries.
Wide application areas
Petrochemical: used for material heating, cooling, condensation and reboiling in refineries and chemical plants;
Power industry: boiler feed water heater, condenser, oil cooler, etc.;
Food and pharmaceutical: milk pasteurization, alcohol condenser, Chinese medicine concentration, etc.;
HVAC: heat transfer equipment in central air conditioning condenser, evaporator and other systems;
Ship and marine engineering: as important devices such as engine coolers and fuel heaters.
With the advancement of industrial energy conservation and intelligent management, shell and tube heat exchangers are developing towards high efficiency, modularization and intelligence. Some new materials such as titanium alloy and stainless steel composite tubes are also widely used in heat exchanger manufacturing to adapt to higher technical requirements and complex working conditions. In addition, real-time management of heat exchange processes through digital monitoring systems is also gradually becoming popular.
Shell and tube heat exchangers have always occupied an important position in the field of heat exchange equipment with their stable and reliable performance, flexible and diverse structures and wide applicability. Whether in traditional industries or in emerging industries such as green energy and new materials, shell and tube heat exchangers will play a key role in improving energy efficiency and promoting technological progress.