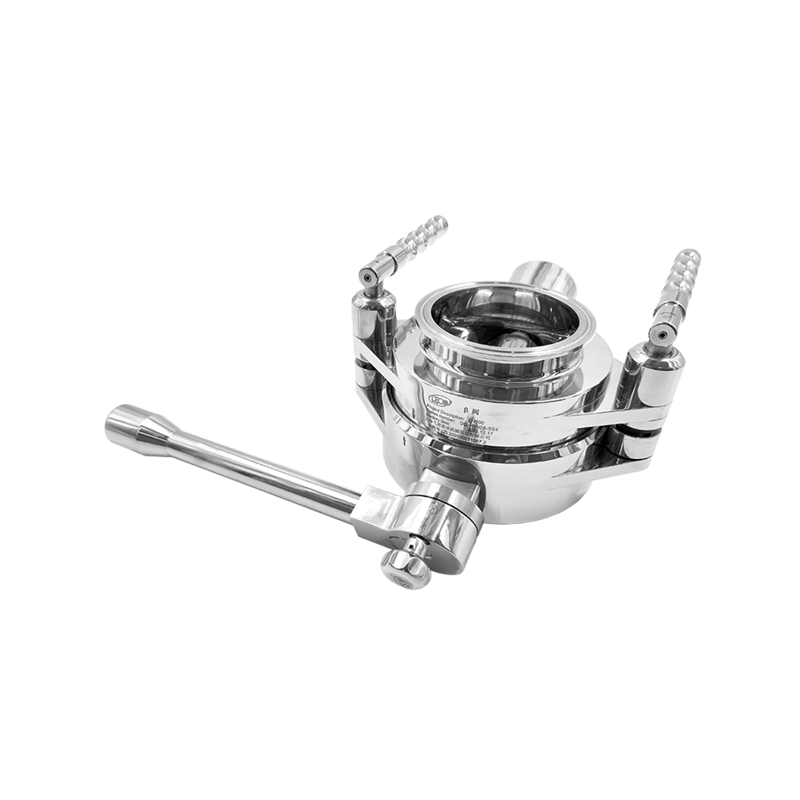
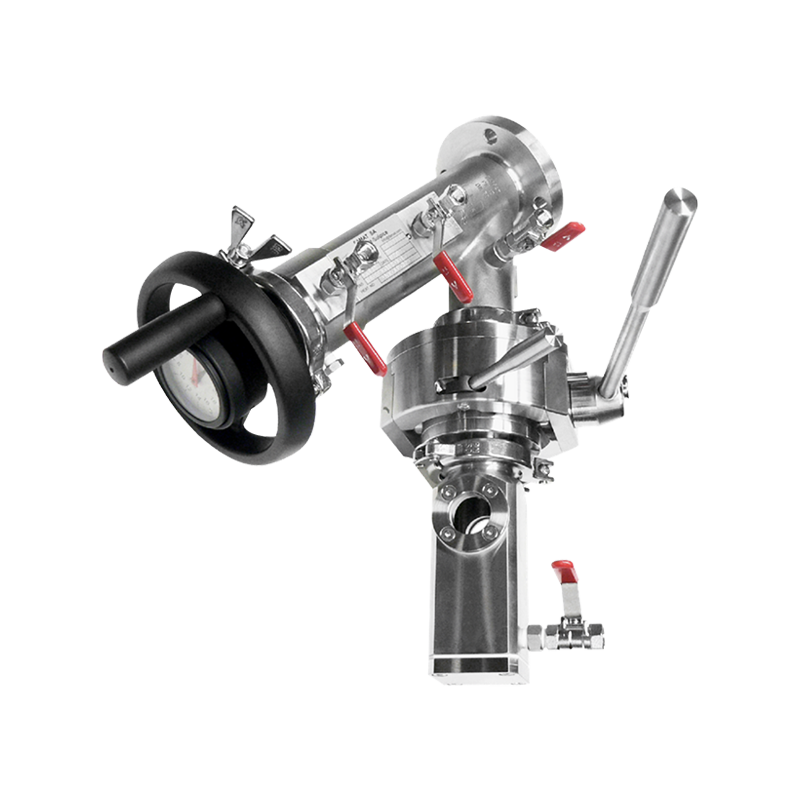
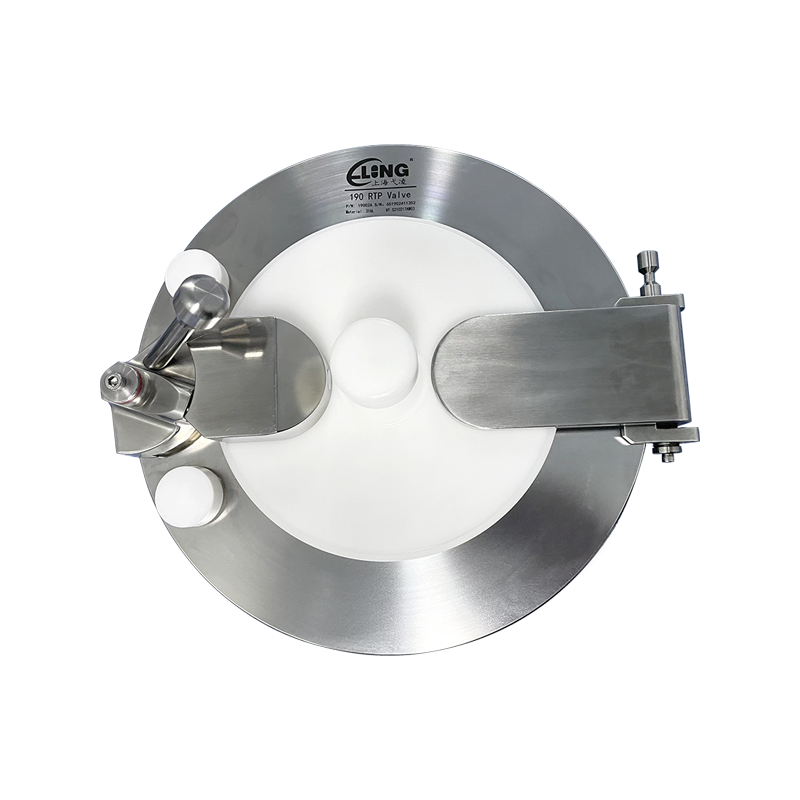
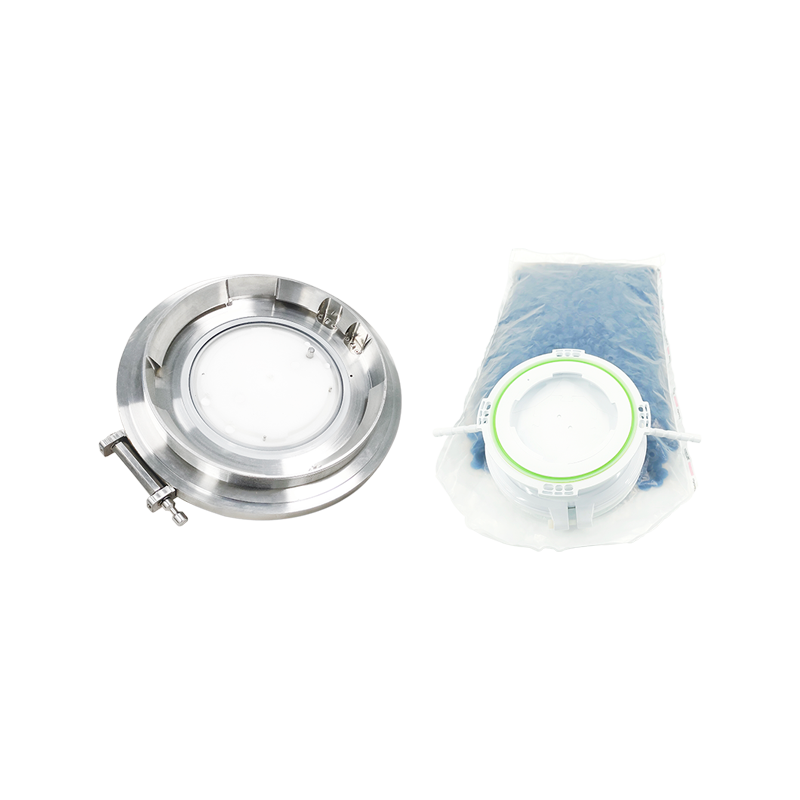
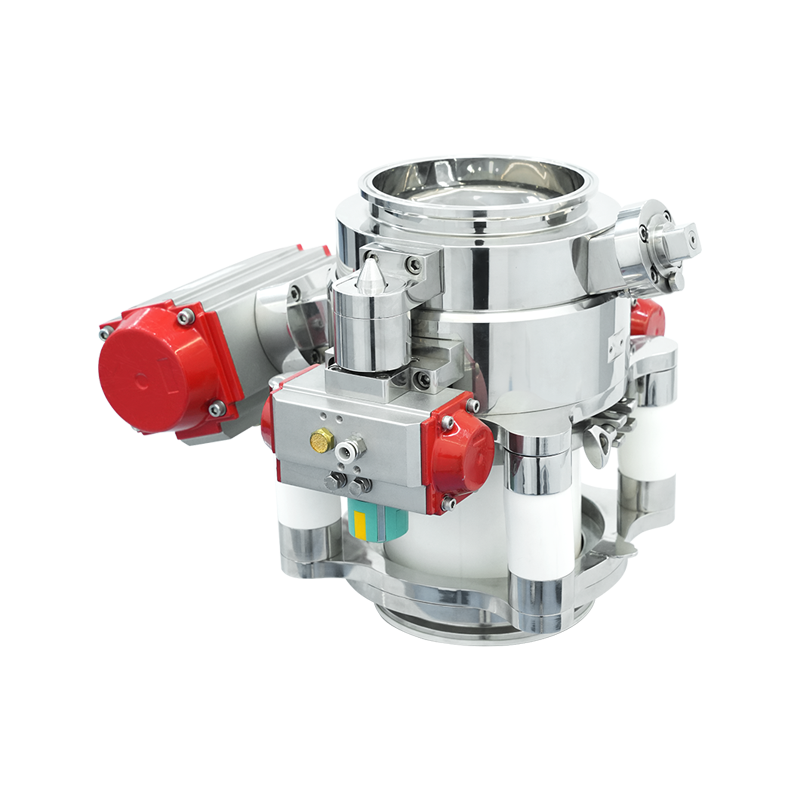
An aseptic transfer RTP valve (Rapid Transfer Port valve) is a critical containment and transfer solution used in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and sterile manufacturing environments. It enables the safe and sterile transfer of materials between isolated systems without exposing products or operators to contamination. RTP valves are widely applied in isolators, restricted access barrier systems (RABS), and cleanroom environments where aseptic integrity is essential.
By creating a sealed interface between two controlled environments, aseptic transfer RTP valves minimize the risk of microbial ingress and cross-contamination. This makes them a key component in modern aseptic processing, where regulatory requirements and patient safety demand strict control over every material transfer step.
Basic Working Principle of RTP Valve Systems
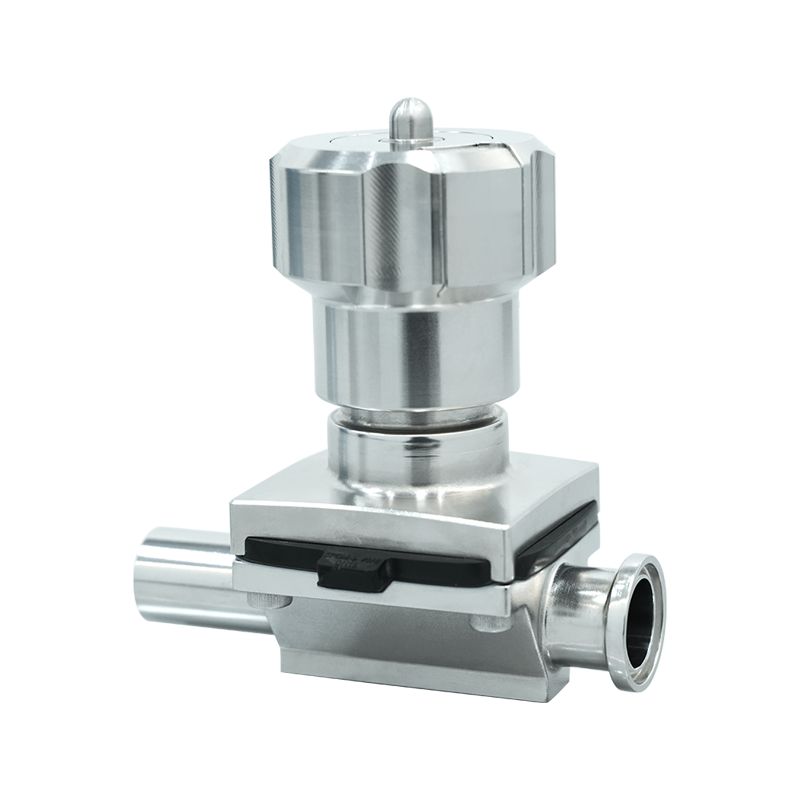
The aseptic transfer RTP valve system typically consists of two main components: the alpha port and the beta container or beta port. The alpha port is permanently mounted on the isolator, filling line, or containment system, while the beta container is attached to the material container or transfer vessel.
During transfer, the alpha and beta components are docked together to form a sealed interface. Once properly docked, both valves open in a controlled sequence, allowing material to pass through while maintaining a sterile barrier between the internal and external environments. After transfer, the valves close and separate, preserving containment on both sides.
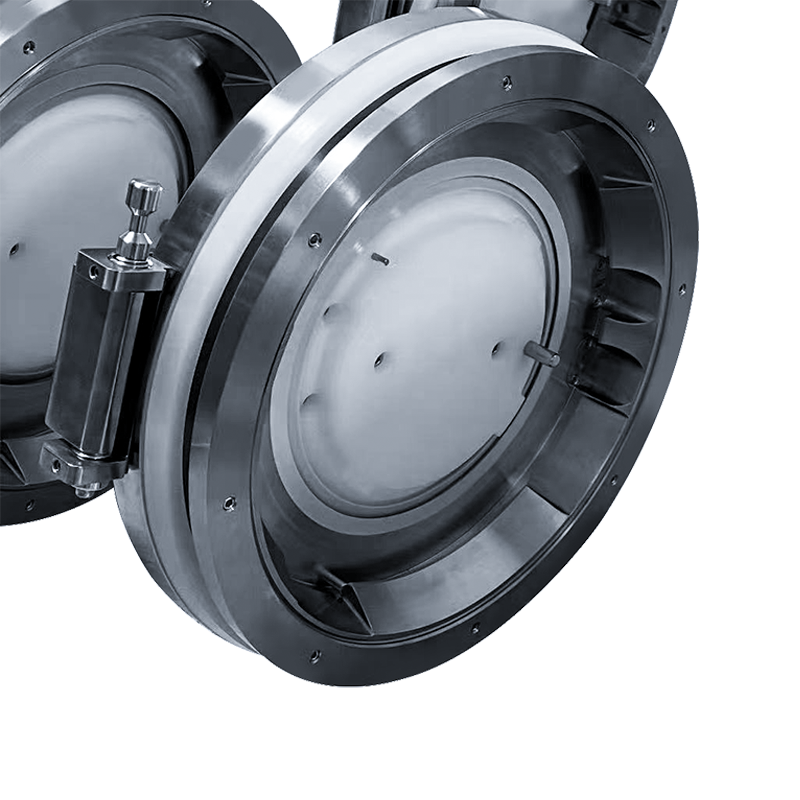

Key Components and Mechanical Design
The mechanical design of an aseptic transfer RTP valve is engineered to provide reliable sealing, repeatable docking, and long-term durability under frequent cleaning and sterilization cycles. Each component plays a specific role in maintaining aseptic conditions.
Alpha Port Assembly
The alpha port is fixed to the isolator or processing equipment. It contains the main sealing surfaces, locking mechanism, and valve door. The alpha port is designed to withstand repeated docking cycles and is often integrated with cleaning-in-place (CIP) or sterilization-in-place (SIP) systems.
Beta Container and Valve Door
The beta container is a removable transfer vessel that carries materials such as sterile components, tools, or product contact parts. The beta valve door mates with the alpha port during docking, forming a continuous sterile boundary. Beta containers are typically designed for easy handling and compatibility with automated or manual transport systems.
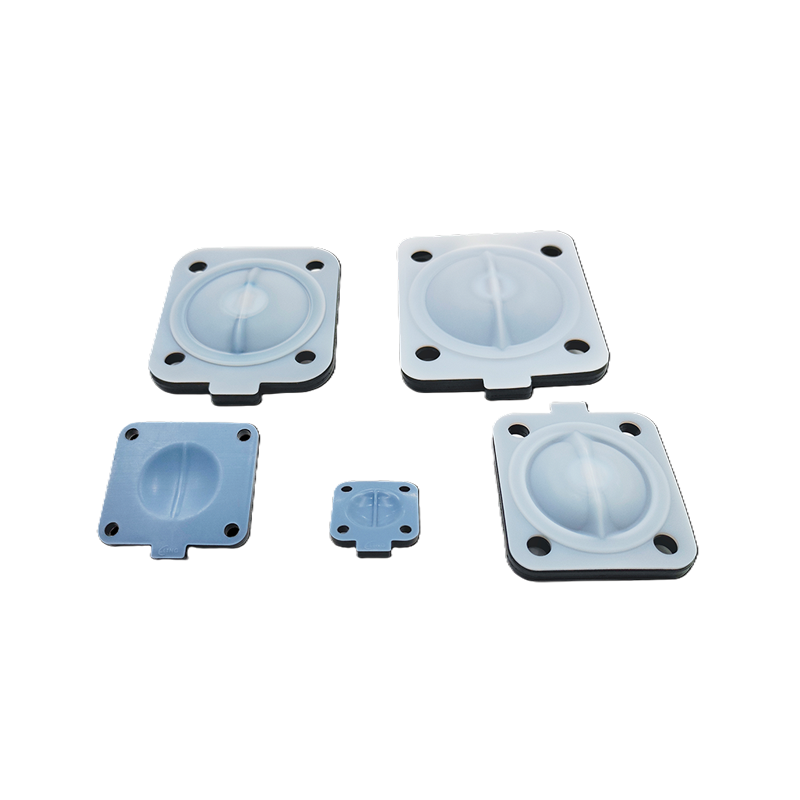
Sealing and Locking Mechanisms
High-performance elastomer or PTFE-based seals are used to maintain airtight and sterile connections. Precision locking mechanisms ensure correct alignment and prevent accidental opening or separation during transfer operations.
Materials of Construction and Surface Finishes
Aseptic transfer RTP valves are manufactured using materials that meet pharmaceutical and biotech standards. Common materials include 316L stainless steel, high-grade polymers, and specialized elastomers for seals and gaskets.
Surface finish is a critical factor in aseptic applications. Polished stainless steel surfaces with low surface roughness help reduce microbial adhesion and support effective cleaning and sterilization. Electropolished finishes are often specified to enhance corrosion resistance and cleanability.
Sterilization and Decontamination Compatibility
A key requirement for aseptic transfer RTP valves is compatibility with standard sterilization and decontamination methods. These valves are commonly designed to withstand vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP), hydrogen peroxide mist, steam, and chemical disinfectants.
Material selection and seal design ensure that repeated exposure to sterilants does not compromise sealing performance or mechanical integrity. This compatibility supports consistent aseptic performance over the life of the equipment.
Common Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biotech Manufacturing
Aseptic transfer RTP valves are used in a wide range of sterile and containment applications where product protection and operator safety are critical.
- Transfer of sterile components into isolators
- Removal of waste and used parts from aseptic zones
- Material transfer in cytotoxic and potent compound handling
- Tool and equipment transfer in sterile processing lines
These applications benefit from the ability of RTP valves to maintain separation between controlled environments while enabling efficient material flow.
Containment Performance and Operator Safety
Beyond aseptic integrity, RTP valves are also designed to provide high levels of containment for hazardous or potent materials. Properly designed systems minimize operator exposure and environmental release during material transfer.
Containment performance is often evaluated using leak testing and surrogate powder tests to verify that the system meets occupational exposure limits and internal safety requirements.
Validation and Regulatory Compliance
Aseptic transfer RTP valves must support regulatory compliance in highly regulated industries. Validation activities typically include installation qualification (IQ), operational qualification (OQ), and performance qualification (PQ).
Documentation related to material traceability, surface finish, cleaning validation, and sterilization compatibility is essential for meeting regulatory expectations from agencies such as the FDA and EMA.
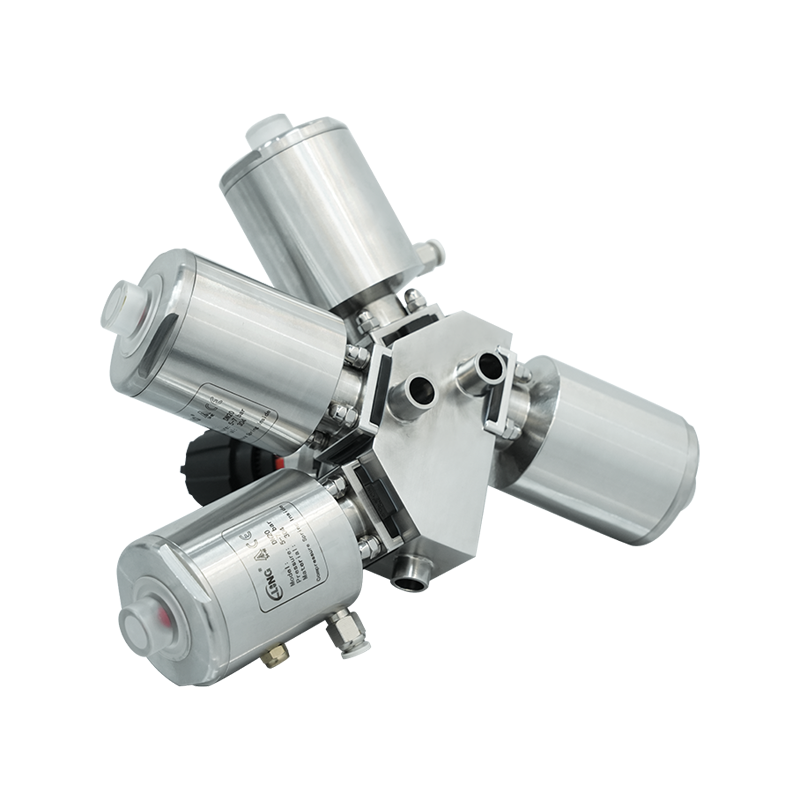
Manual vs. Automated RTP Valve Systems
RTP valves can be operated manually or integrated into automated transfer systems. Manual systems rely on trained operators to dock and undock beta containers, while automated systems use robotics or motorized mechanisms to improve repeatability and reduce human intervention.
Automated RTP systems are increasingly used in high-throughput or high-containment environments, where consistent performance and reduced ergonomic strain are important considerations.
Selection Criteria for Aseptic Transfer RTP Valves
Selecting the right aseptic transfer RTP valve requires careful evaluation of process requirements, facility design, and regulatory expectations. A structured selection approach helps ensure long-term system performance.
- Required transfer size and material volume
- Compatibility with isolator or RABS design
- Sterilization and decontamination methods
- Containment performance requirements
- Validation and documentation support
Working closely with equipment suppliers during the design phase helps ensure proper integration and reduces the risk of costly retrofits.
Installation and Integration into Aseptic Lines
Proper installation of an aseptic transfer RTP valve is essential for maintaining sterile boundaries and mechanical reliability. The alpha port must be correctly aligned and sealed to the isolator or process enclosure.
Integration planning should consider ergonomics, material flow, and cleaning access. Poor placement can lead to inefficient operations, increased risk of operator error, and challenges in routine maintenance.
Maintenance, Inspection, and Lifecycle Management
Routine maintenance and inspection are required to ensure continued aseptic and containment performance. Key maintenance tasks include seal inspection, lubrication of mechanical components, and verification of locking mechanisms.
Lifecycle management strategies often include scheduled replacement of critical wear parts and periodic performance testing. These practices help maintain system reliability and reduce the risk of unexpected failures during production.
Future Trends in Aseptic Transfer Technology
The design of aseptic transfer RTP valves continues to evolve as manufacturers seek higher levels of automation, improved ergonomics, and enhanced data integration. Smart sensors and digital monitoring are increasingly used to track docking cycles, seal integrity, and maintenance status.
These advancements support predictive maintenance strategies and improved traceability, helping facilities achieve higher uptime and stronger regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Ensuring Sterility and Containment with RTP Valves
Aseptic transfer RTP valves are a cornerstone of modern sterile and containment processing. Their ability to maintain aseptic barriers while enabling efficient material transfer supports both product quality and operator safety.
By understanding system design, validation requirements, and operational best practices, manufacturers can implement RTP valve solutions that deliver long-term reliability, regulatory compliance, and process efficiency in demanding pharmaceutical and biotech environments.