In today’s industrial world, precise and reliable flow control is essential for the efficiency, safety, and longevity of countless systems — from chemical processing plants and oil refineries to water treatment facilities and energy production sites. Among the many components that ensure smooth operations, the RTP Valve stands out as a critical innovation. But what exactly is an RTP Valve, and why has it become a trusted choice in advanced fluid handling systems worldwide?
What Is an RTP Valve?
The term RTP Valve typically refers to a “Reinforced Thermoplastic Pipe Valve” or “Reinforced Thermoplastic Polymer Valve”, designed to work seamlessly with RTP pipelines. RTP systems are modern alternatives to traditional steel pipes, offering a corrosion-resistant, lightweight, and durable solution for transporting gases, water, crude oil, and chemicals under high pressure.
An RTP Valve is engineered specifically to match the characteristics of RTP pipelines. It allows operators to start, stop, regulate, or redirect the flow of fluids safely and efficiently. Unlike conventional metal valves, the RTP Valve uses thermoplastic composite materials — such as polyethylene (PE), polyamide (PA), or polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) — sometimes reinforced with glass or carbon fibers to improve strength and performance.
Why Are RTP Valves Gaining Popularity?
Traditional valves, especially those made of metal, have long dominated industrial systems. However, their susceptibility to corrosion, scale buildup, and chemical attack has driven the development of polymer-based alternatives. RTP Valves are increasingly chosen because they offer:
- Corrosion Resistance: Thermoplastic materials resist rust, oxidation, and chemical degradation far better than metals.
- Lightweight Design: Significantly easier to install, transport, and maintain.
- Longer Service Life: With fewer corrosion-related failures, maintenance intervals are reduced.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower lifecycle costs compared to traditional steel valves due to minimal maintenance.
- Environmental Compatibility: Thermoplastics are recyclable and more environmentally friendly to manufacture.
These advantages make RTP Valves especially valuable in industries where aggressive fluids or harsh environmental conditions are common.
How Is an RTP Valve Constructed?
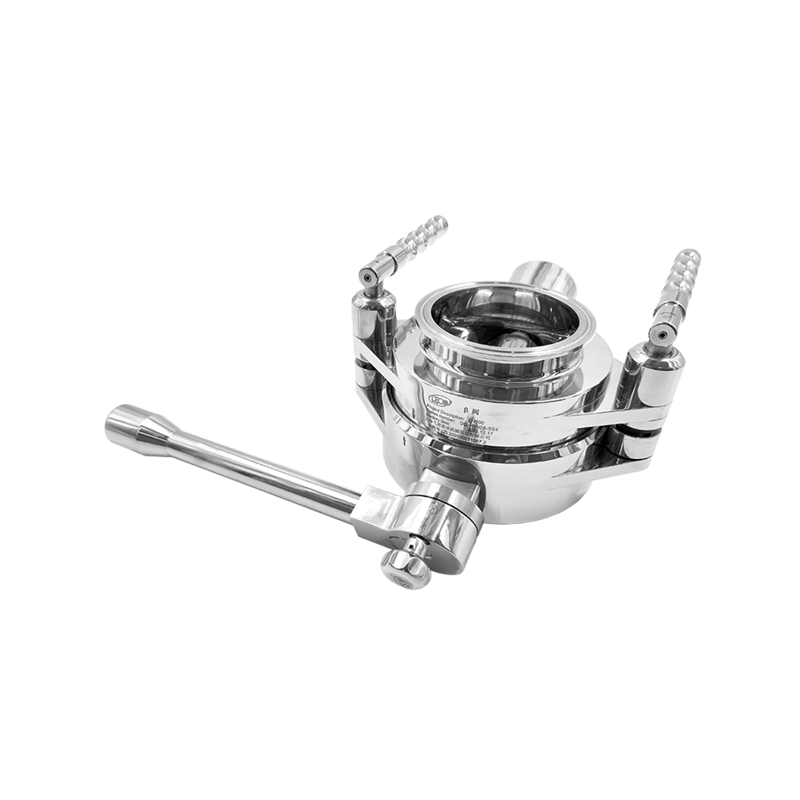
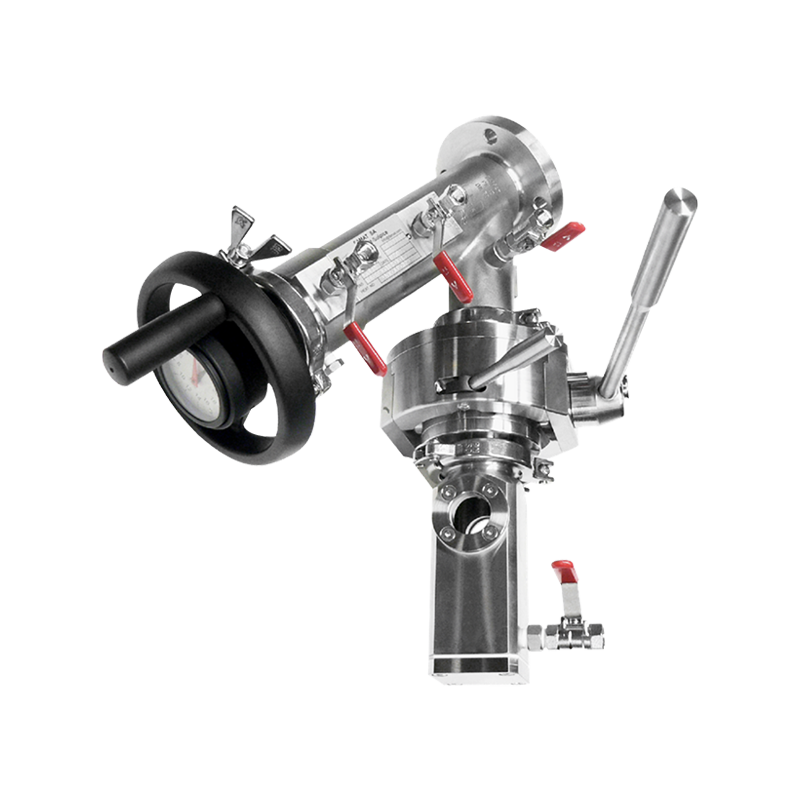
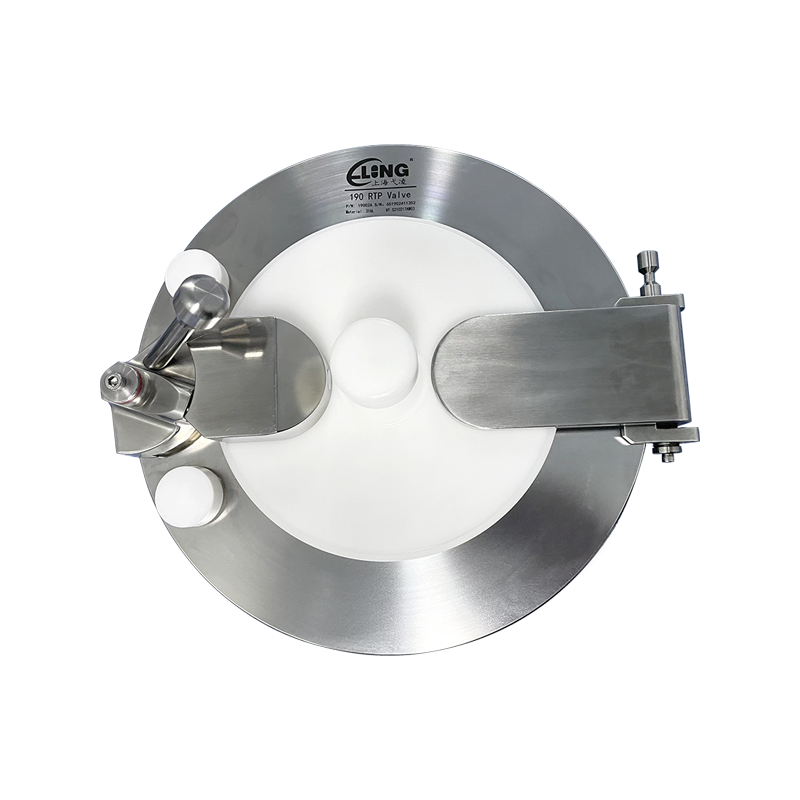
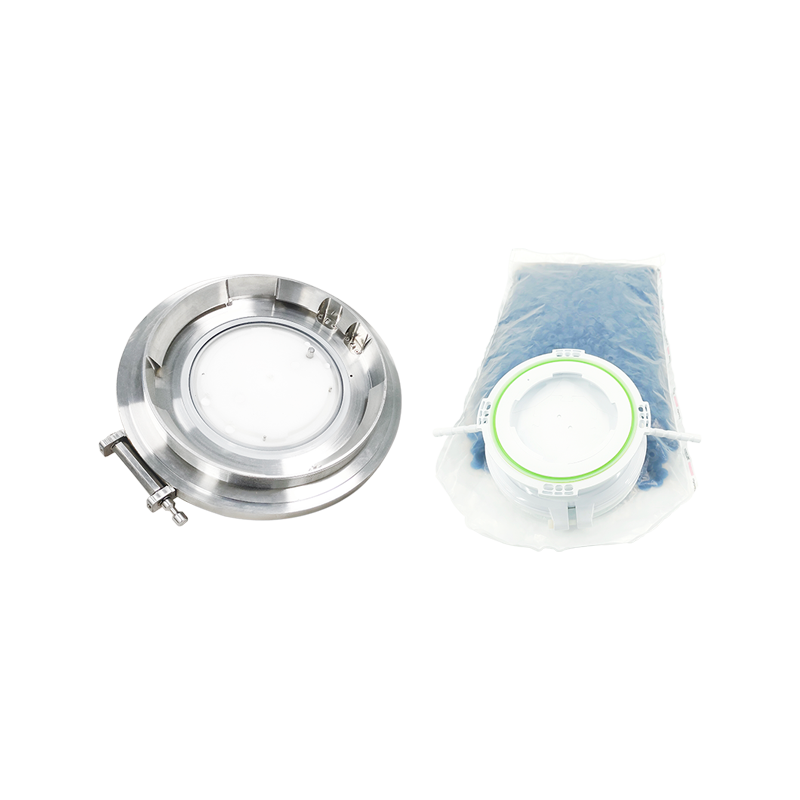
The design and construction of an RTP Valve are both technologically sophisticated and practical. A typical RTP Valve consists of several core components:
-
Valve Body: Made from reinforced thermoplastic materials, the valve body provides structural integrity. Depending on the application, it may be reinforced with carbon fibers or glass fibers for additional strength.
-
Seal and Seat: The internal sealing surfaces are crafted from high-performance elastomers or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), ensuring leak-free operation even under pressure and temperature variations.
-
Stem and Actuator: RTP Valves can be manually operated or automated with pneumatic or electric actuators, allowing precise control of flow.
-
Connection Ends: These are designed to be compatible with RTP pipes, usually through fusion joints, mechanical couplings, or flange connections.
-
Reinforcement Layers: In high-pressure models, additional composite reinforcement ensures the valve maintains its shape and pressure integrity.
This combination of materials and design principles ensures that RTP Valves perform reliably even in challenging industrial environments.
What Are the Key Types of RTP Valves?
Just like traditional valves, RTP Valves come in various types, each serving specific operational needs:
-
RTP Ball Valve:
- Offers full bore flow with minimal pressure drop.
- Ideal for on/off control applications.
- Common in water supply and oil pipeline systems.
-
RTP Gate Valve:
- Provides excellent shut-off capability.
- Suitable for high-pressure operations where complete isolation is necessary.
-
RTP Check Valve:
- Prevents backflow, ensuring unidirectional fluid movement.
- Frequently used in pumping and distribution systems.
-
RTP Butterfly Valve:
- Lightweight and compact, perfect for large-diameter pipelines.
- Used in HVAC, chemical processing, and marine applications.
-
RTP Globe Valve:
- Enables precise flow regulation.
- Commonly found in process control systems where accuracy is critical.
Each valve type can be customized based on size, material, pressure rating, and operational method to suit specific industry requirements.
Where Are RTP Valves Used?
RTP Valves are widely used across various sectors because of their chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and adaptability. Some of the main applications include:
-
Oil and Gas Industry:
- Transporting crude oil, natural gas, and produced water.
- Resisting corrosion from H₂S, CO₂, and saline environments.
-
Chemical Processing Plants:
- Handling aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents safely.
- Reducing maintenance downtime and preventing leaks.
-
Water and Wastewater Treatment:
- Used in potable water distribution, desalination, and sewage systems.
- Prevents rust contamination and ensures hygienic flow.
-
Mining Operations:
- Managing slurry, tailings, and process water under harsh, abrasive conditions.
-
Renewable Energy:
- Supporting geothermal and hydrogen transport systems where corrosion resistance is vital.
-
Agriculture and Irrigation:
- Reliable fluid control in large-scale irrigation systems due to their lightweight and weather-resistant properties.
How Do RTP Valves Improve Operational Efficiency?
Efficiency in fluid systems isn’t just about moving liquids or gases — it’s about minimizing losses, reducing downtime, and ensuring safe operation. RTP Valves enhance efficiency in multiple ways:
- Smooth Internal Surface: The thermoplastic liner provides a low-friction flow path, minimizing pressure loss and improving fluid velocity.
- Leak-Free Performance: High-quality seals prevent leakage, saving energy and fluid resources.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: No rusting or scaling means less frequent servicing and replacement.
- Lightweight Installation: Reduces labor costs and simplifies handling in remote locations.
For industries looking to improve sustainability and reliability, these efficiency benefits make RTP Valves a strong investment.
What About Pressure and Temperature Resistance?
One of the misconceptions about thermoplastic valves is that they cannot handle high pressures or temperatures. However, modern RTP Valves are specifically engineered to withstand these challenges:
- Pressure Resistance: Depending on the design, RTP Valves can handle pressures up to 150 bar (or higher for reinforced versions).
- Temperature Range: Most RTP materials perform well between -40°C and +100°C, making them suitable for a wide variety of environmental conditions.
Special versions made from advanced polymers like PPS or PEEK can tolerate even higher temperatures while maintaining chemical resistance.
How Are RTP Valves Tested for Quality and Safety?
To ensure reliability, RTP Valves undergo rigorous quality control processes before being approved for industrial use. Common tests include:
- Hydrostatic Pressure Testing: Ensures the valve can withstand maximum operating pressure without leaks or deformation.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Simulates extreme temperature changes to assess material stability.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluates performance when exposed to acids, bases, and solvents.
- Fatigue and Burst Testing: Determines the valve’s lifespan under repeated stress conditions.
Meeting or exceeding international standards such as ISO, API, and ASTM ensures that RTP Valves deliver consistent performance in critical applications.

Are RTP Valves Environmentally Friendly?
Yes — one of the standout advantages of RTP technology lies in its sustainability.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Manufacturing thermoplastic valves requires less energy than producing steel valves.
- Recyclable Materials: Many RTP components can be reused or recycled after service life.
- Corrosion-Free Design: Eliminates the need for anti-corrosion coatings or chemical treatments, which can harm the environment.
For industries aiming to meet modern environmental standards, RTP Valves support both operational performance and ecological responsibility.
What Are the Limitations of RTP Valves?
Although RTP Valves offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations to consider:
- Temperature Restrictions: While they perform well up to 100°C, extremely high-temperature environments may still require metal alternatives.
- Cost: Advanced thermoplastic materials can be more expensive initially, though lifecycle savings often offset this cost.
- Pressure Rating Limits: Ultra-high-pressure applications may demand hybrid designs that combine thermoplastic and metal components.
Manufacturers continue to innovate, however, creating RTP Valves with improved high-temperature and high-pressure capabilities to expand their range of applications.
Conclusion: Why Are RTP Valves the Future of Fluid Control?
In a world that increasingly demands efficiency, durability, and sustainability, RTP Valves represent a transformative solution in fluid control technology. Their combination of lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, environmental compatibility, and long service life makes them a smart choice for a wide range of industries — from oil and gas to water treatment and renewable energy.
While metal valves have dominated the past, the future of pipeline systems clearly belongs to advanced materials like reinforced thermoplastics. As technology evolves, RTP Valves will continue to play a vital role in enabling safer, cleaner, and more efficient fluid management across global industries.