In high-containment environments such as pharmaceutical production, biotechnology research, and nuclear facilities, safety and sterility are top priorities. One critical device that ensures both is the Rapid Transfer Port (RTP). It allows for the secure and contamination-free transfer of materials into or out of an isolated containment area without compromising environmental or product integrity.
This technology is especially crucial in Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) cleanrooms, isolators, and biosafety environments where maintaining a strict barrier between controlled and uncontrolled areas is mandatory.
1. What is a Rapid Transfer Port?
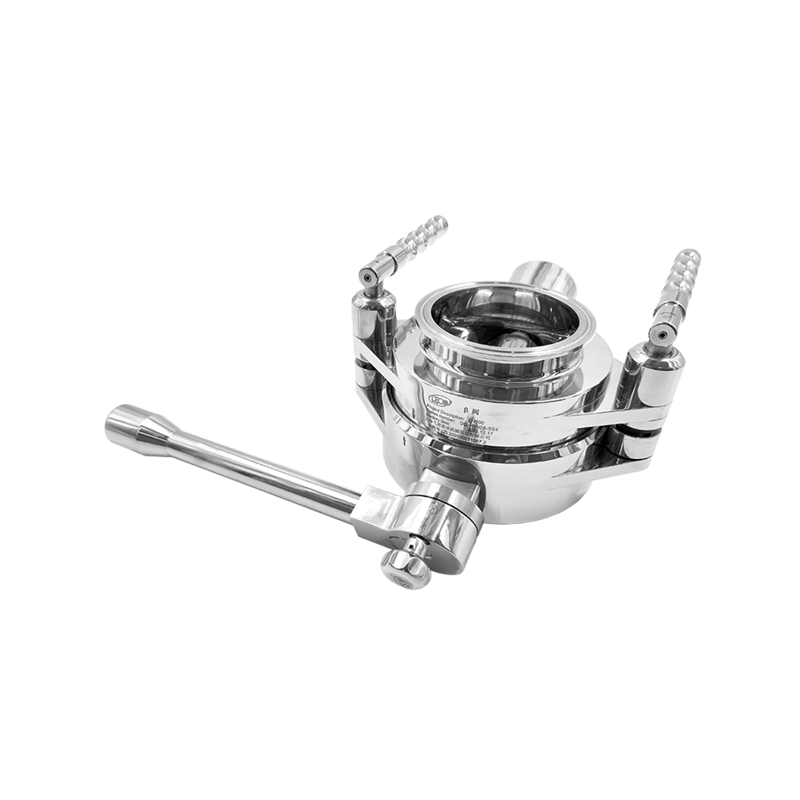
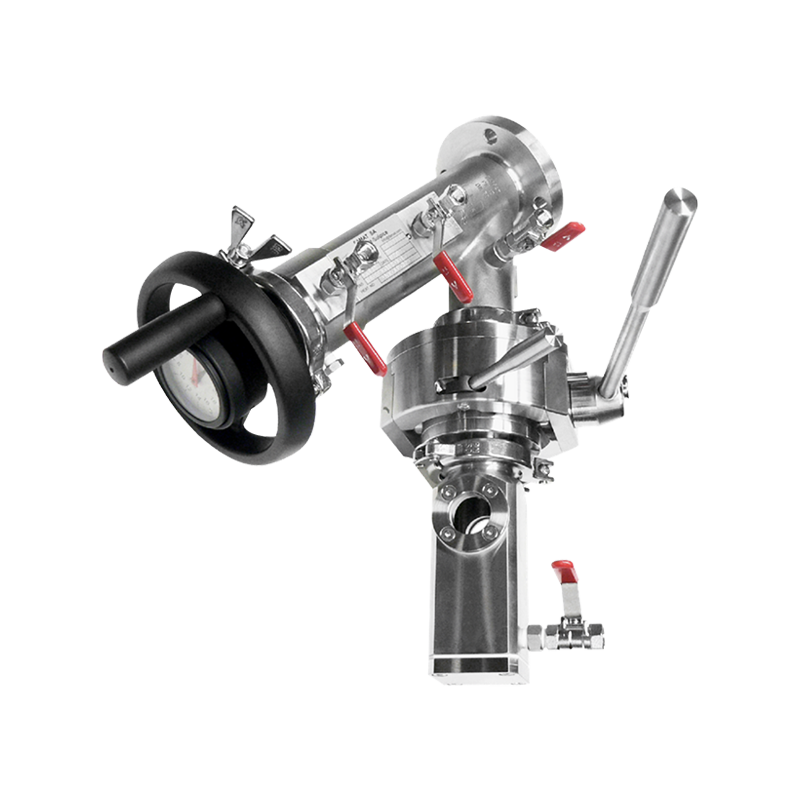
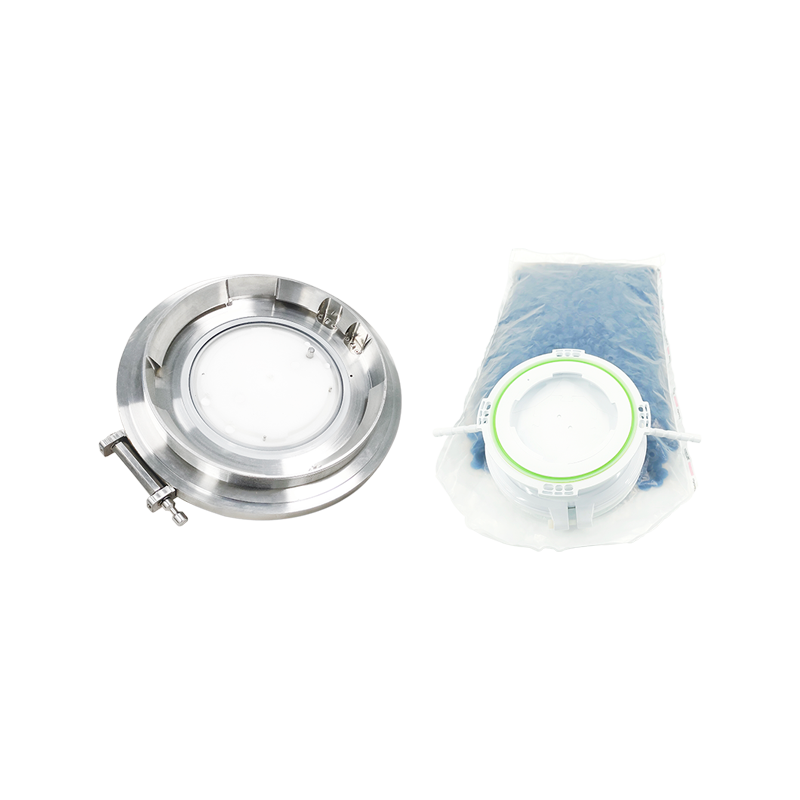
A Rapid Transfer Port is a sealed mechanical interface that enables the movement of products, tools, or samples between different containment zones. It works by using a double-door system: one door is mounted on the containment system (the alpha port), and the other door is attached to a mobile container or bag (the beta container). When the two connect, they form a single secure passage, preventing contaminants from escaping or entering.
The mechanism ensures:
- No direct exposure of the contents to the external environment.
- Minimal contamination risk to operators.
- Preservation of sterile or hazardous conditions inside the containment system.
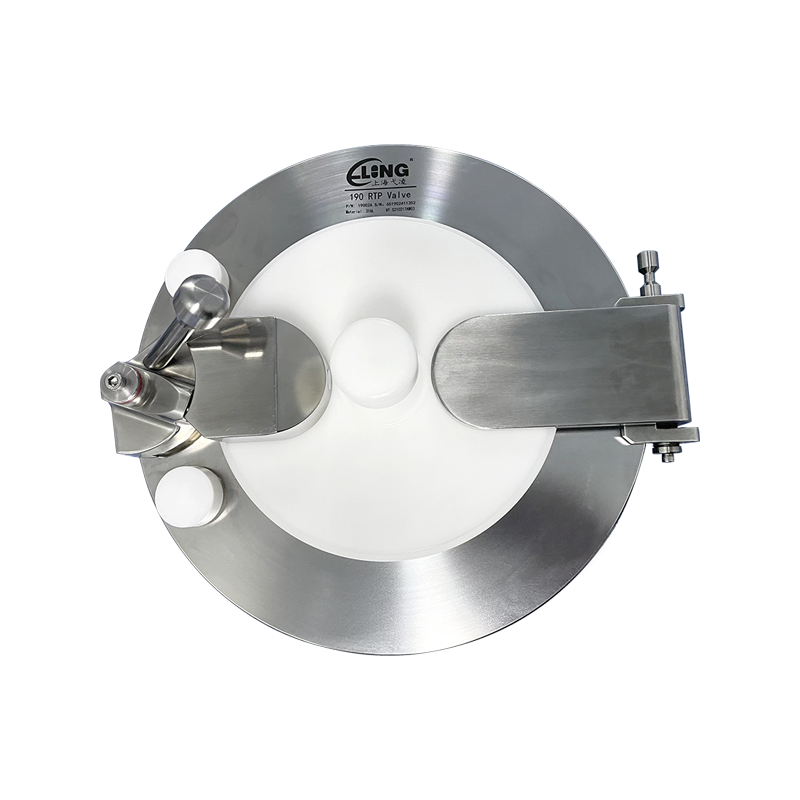

2. How Does a Rapid Transfer Port Work?
The RTP operation involves several steps:
- Docking – The beta container is aligned with the alpha port and locked into position.
- Door Interlock – Both doors are mechanically interlocked to prevent accidental opening.
- Opening – Once secure, the doors open simultaneously, creating a sealed channel.
- Transfer – Materials are moved through the channel without breaching containment.
- Closing – Both doors close together before the units are separated.
- Undocking – The beta container is removed for cleaning or disposal.
This design is especially popular in environments that handle hazardous drugs, cytotoxics, or sterile pharmaceutical components.
3. Key Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Double-door sealing system | Prevents contamination during material transfer. |
| Compatibility with disposable systems | Reduces cleaning validation time and cross-contamination risk. |
| Ergonomic operation | Simple docking and undocking process, reducing operator fatigue. |
| High containment performance | Can achieve OEB5 (Occupational Exposure Band) containment levels. |
| Durable construction | Built from stainless steel or high-grade polymers for long service life. |
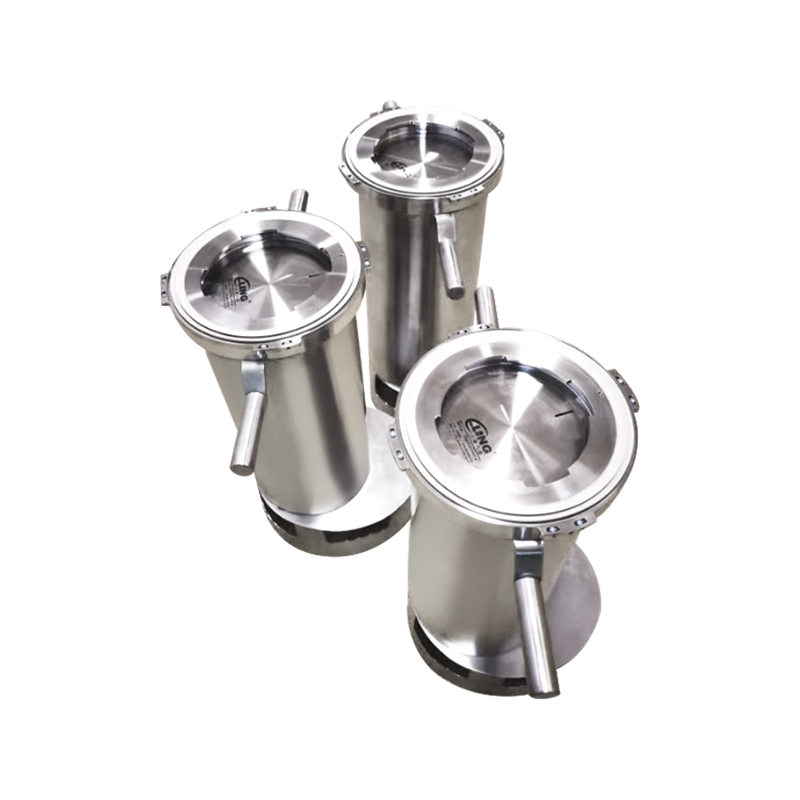
| Custom sizes available | Adapts to different container volumes and process needs. |
4. Applications of Rapid Transfer Ports
RTPs are widely used in industries where containment and sterility are critical:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing – For aseptic transfer of sterile components, raw materials, and finished products.
- Biotechnology – Moving sensitive biological samples without contamination.
- Nuclear Industry – Handling radioactive substances with minimal exposure risk.
- High-containment Laboratories – In BSL-3 and BSL-4 labs for handling infectious agents.
- Medical Device Production – Transferring sterile equipment parts during assembly.
5. Compliance and Safety Standards
Modern RTP systems are designed to comply with ISO, GMP, and FDA guidelines. They often undergo rigorous integrity testing such as:
- Leak tests (to confirm sealing performance)
- Particle count monitoring
- Pressure decay tests
These ensure that the system maintains a reliable barrier between environments.
6. The Future of Rapid Transfer Port Technology
With the increasing focus on operator safety and process sterility, RTP technology is evolving toward:
- Single-use beta containers for faster turnaround and reduced cleaning needs.
- Automation integration with robotic handling in isolators.
- Smarter monitoring with built-in sensors for leak detection.
- Lightweight composite materials for easier operation and reduced wear.
Conclusion
The Rapid Transfer Port has become an indispensable tool in high-containment industries. By providing a secure, contamination-free transfer between zones, it enhances product quality, ensures operator safety, and supports regulatory compliance.