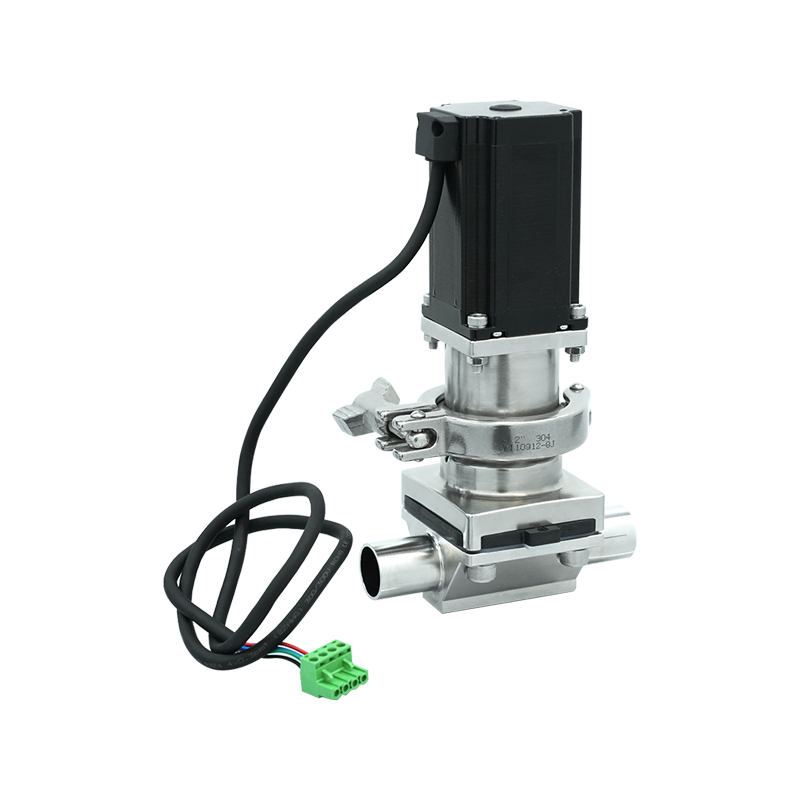
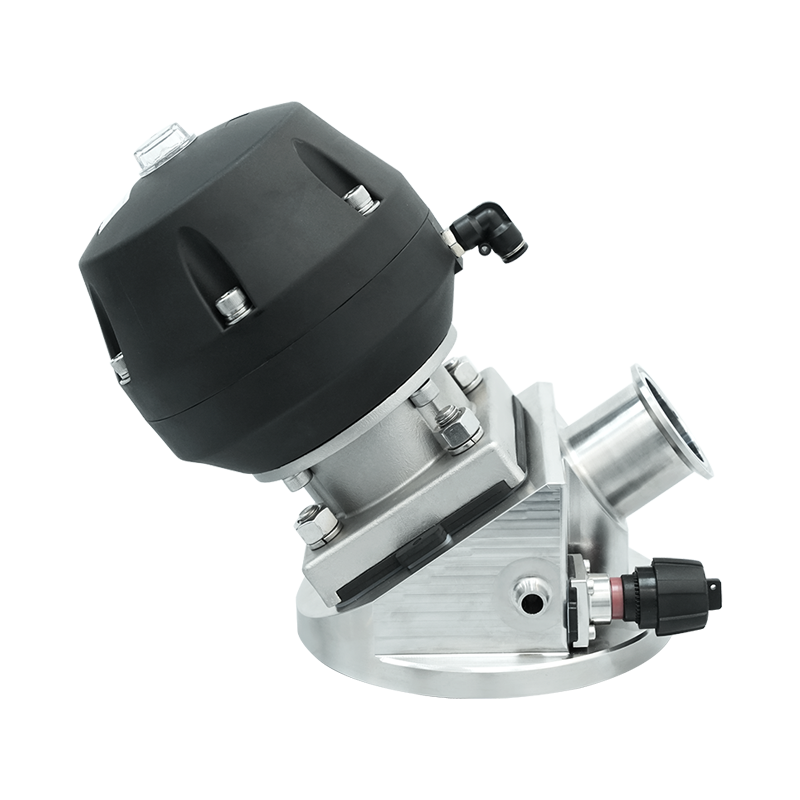
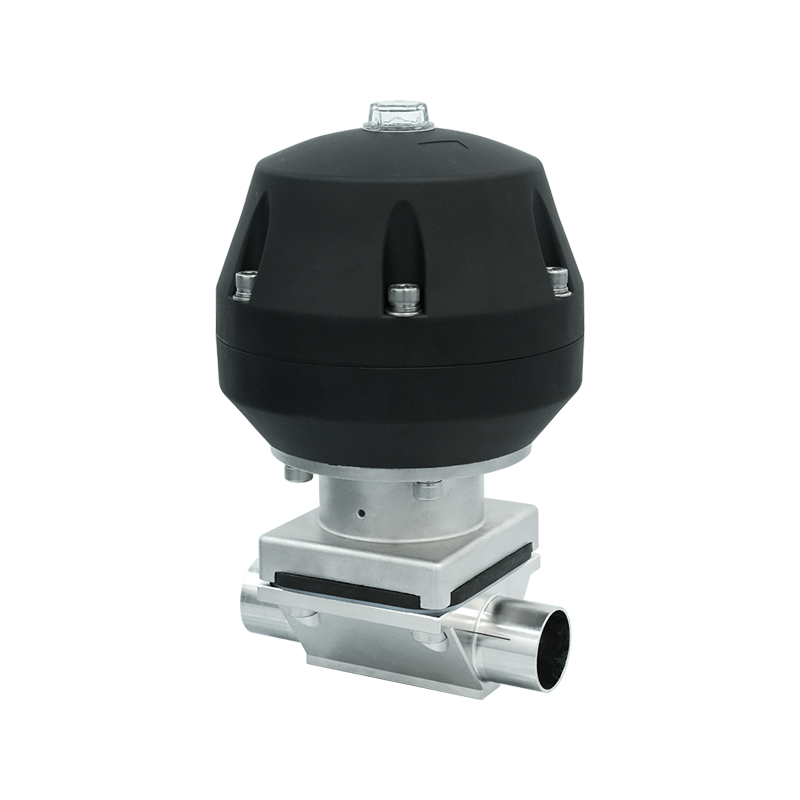
Introduction to Fermentation Process Valves
Fermentation process valves are essential components in bioreactors and fermenters, ensuring precise control of liquids, gases, and pressure throughout the fermentation cycle. Selecting the right valve type is crucial for maintaining product quality, efficiency, and safety. Two common types are manual valves and automated valves, each offering distinct advantages and applications.
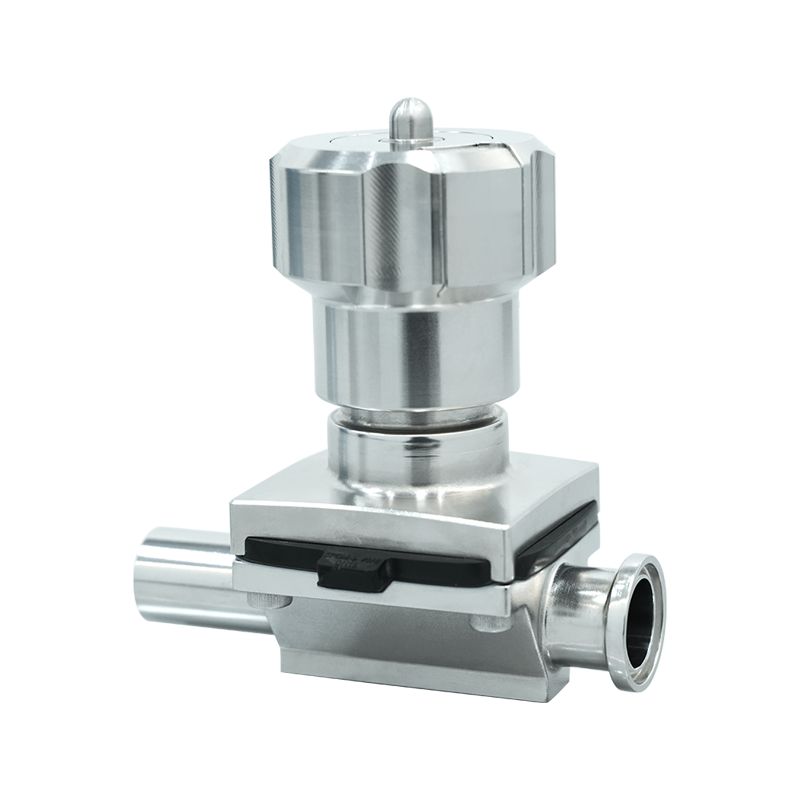
Overview of Manual Fermentation Process Valves
Manual fermentation process valves are operated by hand, using levers, wheels, or handles to control the flow of fluids or gases within the fermentation system. They are often favored in smaller-scale operations or situations where automation is unnecessary or cost-prohibitive.
Key Features of Manual Valves
- Simple design with minimal moving parts.
- Low initial cost and easy replacement.
- Direct operator control for immediate adjustments.
- Suitable for low-frequency operations and small fermenters.
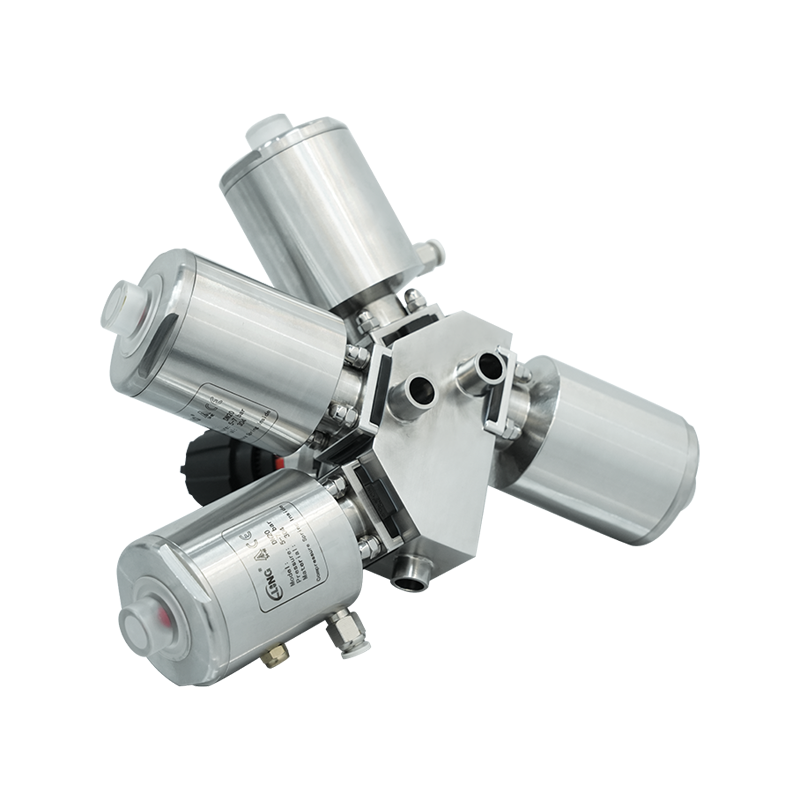
Overview of Automated Fermentation Process Valves
Automated fermentation process valves use actuators, sensors, and control systems to regulate fluid and gas flow automatically. These valves are integral to modern industrial fermentation, allowing for precise, repeatable, and remote-controlled operations.
Key Features of Automated Valves
- Integrated with PLC or SCADA systems for process automation.
- Provides accurate flow, pressure, and temperature control.
- Reduces human error and improves product consistency.
- Suitable for high-frequency operations and large-scale fermentation.
Comparison Between Manual and Automated Valves
Choosing between manual and automated fermentation process valves depends on the scale of production, precision requirements, and budget. The table below highlights the main differences:
| Feature | Manual Valve | Automated Valve |
| Operation | Hand-operated | Actuator-controlled |
| Precision | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Low initial cost | High initial cost |
| Maintenance | Simple, low-tech | Requires calibration and technical knowledge |
| Suitability | Small-scale or low-frequency fermenters | Large-scale, high-frequency, or automated systems |
Operational Advantages of Automated Valves
Automated valves offer several advantages that improve efficiency and consistency in fermentation processes:
- Remote monitoring and control reduce the need for constant operator presence.
- Real-time adjustments to pressure, flow, and temperature optimize fermentation conditions.
- Integration with data systems provides process analytics and predictive maintenance.
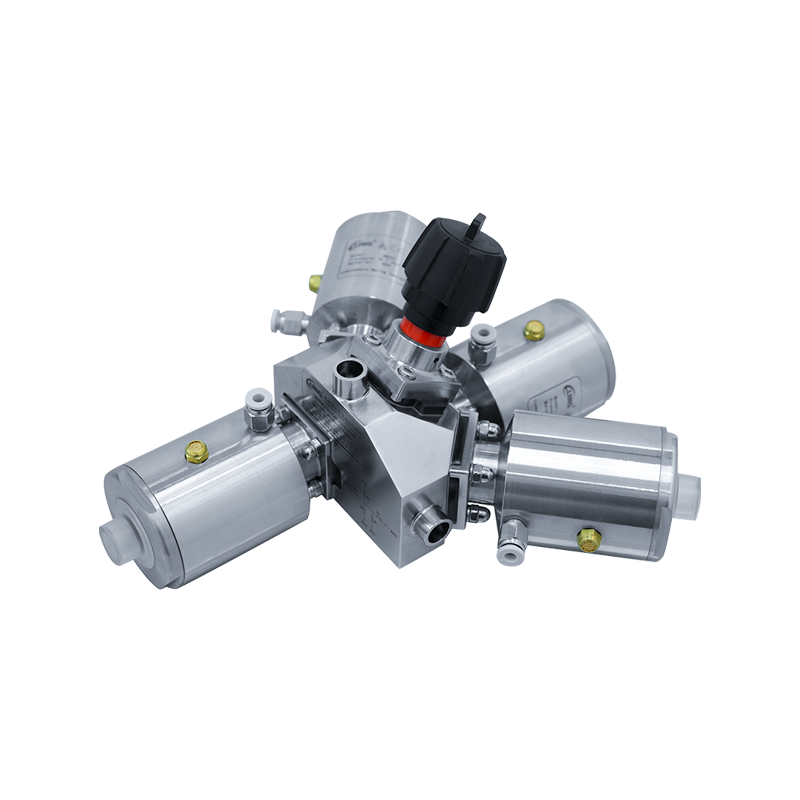
Maintenance Considerations
Manual and automated valves require different maintenance approaches to ensure reliable operation. Manual valves are simple to inspect and repair, while automated valves need specialized technical knowledge for calibration and troubleshooting.
- Regular lubrication of moving parts is essential for manual valves.
- Actuator and sensor calibration must be performed periodically for automated valves.
- Both types require inspection for leaks, corrosion, and seal integrity.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While automated valves have a higher upfront cost, their precision, efficiency, and reduced labor costs often justify the investment in large-scale or high-value fermentation processes. Manual valves, with their simplicity and affordability, remain practical for smaller operations or processes with minimal automation requirements.
Conclusion
Both manual and automated fermentation process valves play vital roles in controlling bioreactor operations. Manual valves provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while automated valves deliver precision, consistency, and efficiency for large-scale industrial fermentation. Selecting the appropriate valve type depends on process requirements, scale, and desired level of automation, ensuring optimal performance and product quality.