In highly clean industrial production processes such as biopharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and sterile medical products, the transfer and packaging of materials need to minimize particle contamination and microbial risks. RTP Beta Bag is a high-level clean delivery solution born in this context.
1. What is RTP Beta Bag?
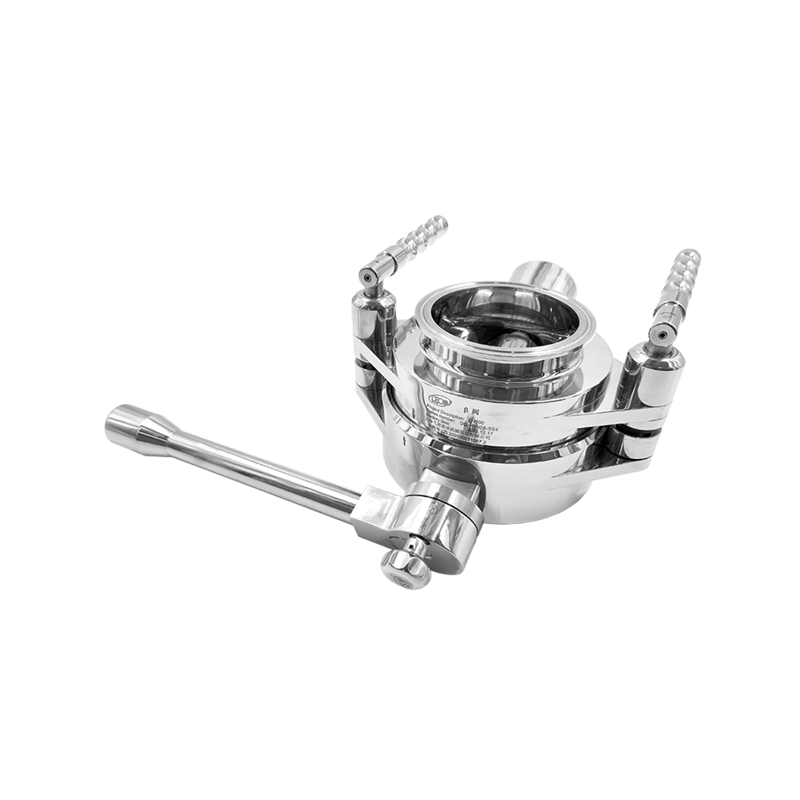
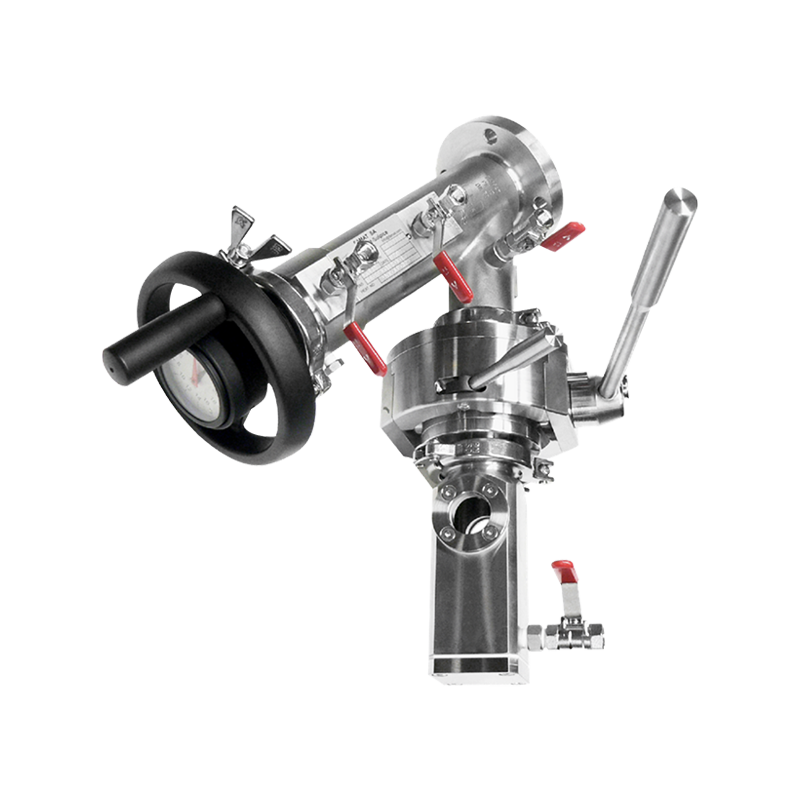
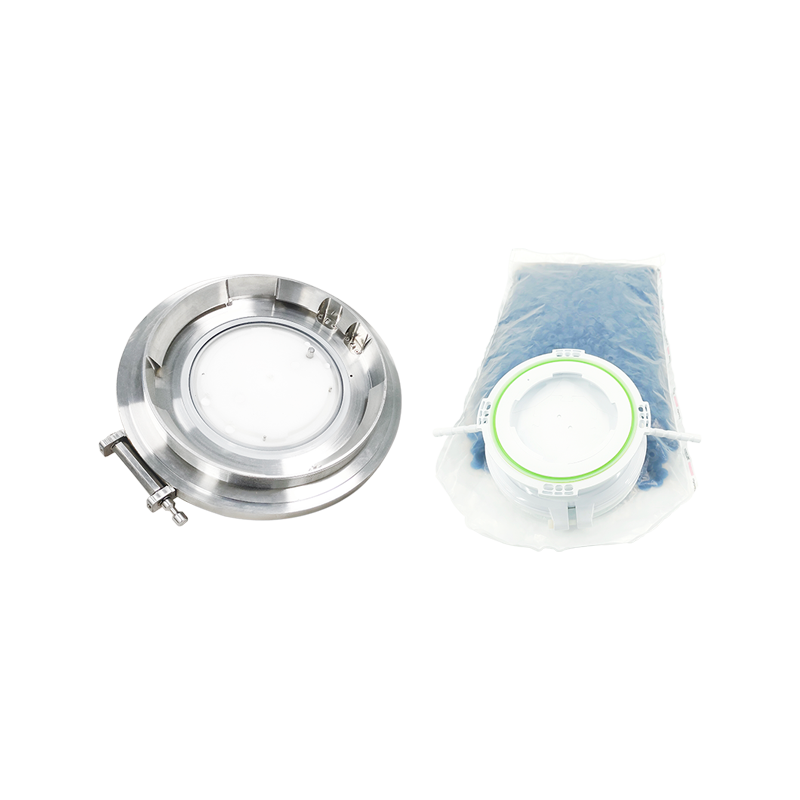
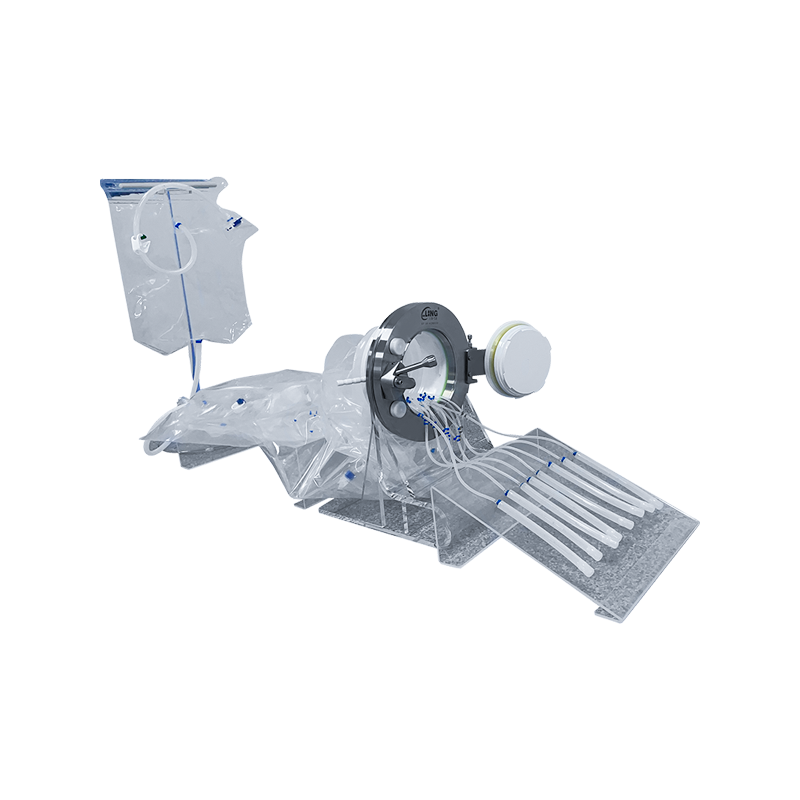
RTP Beta Bag is a flexible packaging container for closed material transfer. It is used with the RTP Alpha Port system to achieve safe transfer of materials, tools or products between two systems in aseptic or high-purity environments.
The "Beta" in "Beta Bag" refers to its "passive side" docking to the "Alpha Port" (active side). Its structure integrates connectors and sealing flanges, enabling fast, safe, and contamination-free transfer during docking.
The RTP system was first used in the nuclear industry to safely transfer radioactive materials and is now widely used in:
Biopharmaceuticals (such as aseptic filling, stock solution transfer)
Medical device sterilization packaging
Sterile reagent package transfer
Cell culture and GMP laboratory operations
Semiconductor production clean room
2. What are the components of the RTP Beta Bag?
High cleanliness level bag
Usually made of multi-layer medical-grade polymer film (such as PE, TPU, etc.), with high barrier properties, chemical corrosion resistance, and low particle release performance.
Can be designed as a single layer or multiple compartments, and can pre-package sterile tools, filters, culture media, etc. as needed.
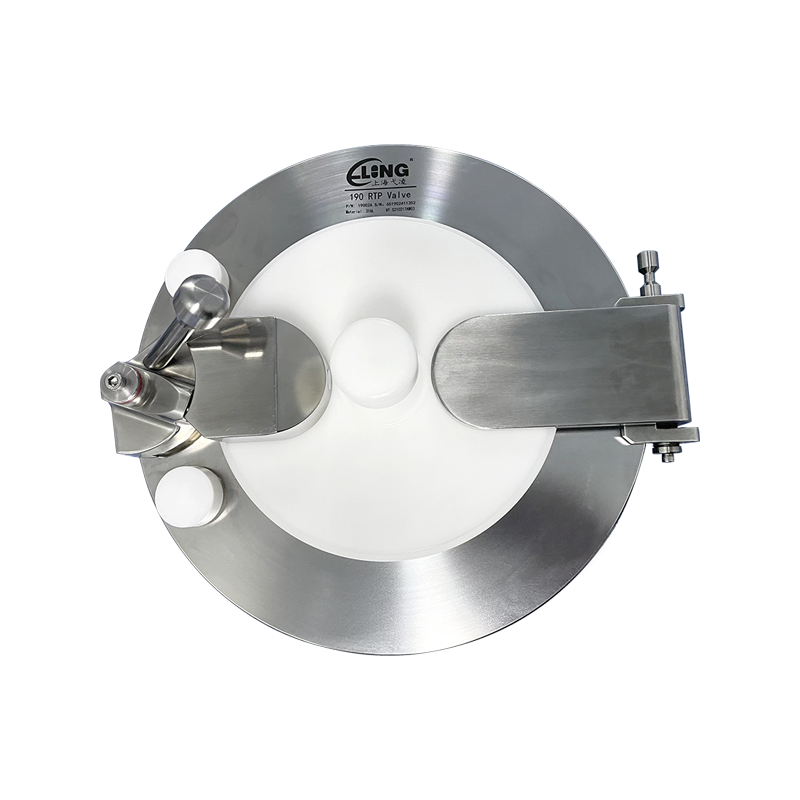
Beta Flange
Fixed at the opening of the bag body, used in conjunction with the Alpha Port to ensure mechanical and sealed docking.
Using 316L stainless steel or high-performance plastics (such as PPSU), high temperature resistance, irradiation sterilization.
Docking seal and locking mechanism
Ensure no leakage and cross contamination during the transfer process.
It can realize twisting and twist-lock connection to meet the requirements of sterile GMP.
3. How does RTP Beta Bag realize aseptic transfer?
The docking steps (typical process) are as follows:
Beta Bag preparation
Package the required items in a clean environment, seal and sterilize with gamma rays or ETO.
Connect to Alpha Port
Align the Beta flange with the Alpha Port inlet, rotate and lock to form an airtight connection.
Opening operation
The door panels on both sides of Alpha and Beta are opened at the same time to form a common sterile cavity to achieve the transition between sterile areas.
Material transfer
Transfer the items in the bag to the system or reversely transfer them to the bag (such as transferring contaminated samples).
Disconnection
Close the door panel, loosen the connecting flange, remove the empty bag or the full Beta Bag, and the transfer is completed.
The system ensures that the operator does not need to touch the contents, and the entire process is completed without destroying the sterile barrier, avoiding the risk of contamination and exposure.
4. What are the advantages of RTP Beta Bag compared with traditional transfer methods?
| Features | RTP Beta Bag | Traditional transfer method |
| Sterility protection | Complete isolation and double-door docking to avoid any external contamination | Mostly require an open environment with air or manual contact |
| Security | Sealed operation to protect personnel and samples | Possible biological or chemical exposure risk |
| Operational efficiency | Quick connection and disconnection, strong repeatability | Manual transfer is cumbersome and difficult to standardize |
| compatibility | Can be seamlessly connected with various RTP Alpha Ports | Different systems, poor compatibility |
| Scope of application | Biopharmaceuticals, semiconductors, nuclear industry, medical | Mostly used in conventional laboratories or environments without clean requirements |
5. What are the typical application scenarios of RTP Beta Bag?
1. Biopharmaceuticals
Transfer of sterile stock solution and freeze-dried powder
Input of pre-sterilized packaging materials in filling lines
Packaging input of process consumables (such as filters, pipes, connectors)
2. Cell therapy and genetic engineering laboratories
For the transfer of sterile cell samples
Sterile input/output of culture media and reagents in the laboratory
3. Medical equipment industry
Sterilized instruments, tools, etc. enter the sterile operation area after sterilization
Isolated transfer of high-risk waste
4. Semiconductor and microelectronics manufacturing
Clean transfer of wafer boxes, photomasks or detection probes
Reducing static electricity and microparticle contamination
5. Nuclear industry
Transfer and isolation of high-risk radioactive materials
Non-exposure packaging system for radioactive samples
6. how to choose the right RTP Beta Bag?
Size and capacity
Choose the appropriate bag specifications according to the volume and shape of the pre-packaged contents.
Material compatibility
Different applications (such as chemical resistance, heat resistance, antistatic) require different material membrane layers and flanges.
Connection Standard
Confirm that the interface standard of the Alpha Port (usually 105mm, 190mm, 270mm, etc.) is compatible with the Beta flange.
Sterilization method
It is necessary to consider whether the product can accept processes such as gamma ray, ethylene oxide or high-temperature steam sterilization.
Whether customization is required
If you need to encapsulate specific tools, manage by batch number, label traceability, etc., you need to negotiate with the supplier for customized services.
7. Is the RTP Beta Bag reusable?
The original design of the Beta Bag is "single-use" to avoid the risk of cross-contamination. Although its Beta flange may be made of highly durable materials, it is generally not recommended to reuse it considering the stringent requirements of sterile control and verification costs.
Some high-end bag systems use a replaceable bag + repeatable flange structure, but they still need to be strictly cleaned and verified under high clean conditions.
8. Development trend of RTP Beta Bag
With the rapid development of biomedicine, precision manufacturing and high-purity materials industries, the RTP Beta Bag system is also constantly upgrading:
More intelligent integrated design
Integrate traceability systems such as RFID tags and QR codes to achieve batch tracking and compliance records.
Development of high-functional membrane materials
Multilayer membrane materials with stronger mechanical strength, barrier properties and environmental adaptability will gradually replace traditional membrane materials.
Modularity and rapid customization
Customers' demand for flexible loading and rapid production has prompted manufacturers to develop more standardized and modular customization solutions.
Environmentally friendly and degradable design
Environmentally friendly Beta Bags that decompose under controllable conditions are becoming a new trend in green GMP workshops.
9. Conclusion: Why is RTP Beta Bag an indispensable part of clean production?
In the current context of increasing global requirements for sterile, pollution-free and efficient production, RTP Beta Bag is no longer just a packaging bag, but a "bridge" connecting clean areas and production process safety. It solves many pain points of traditional transfer methods in terms of efficiency, cleanliness and traceability, and becomes a key equipment for achieving GMP standards, reducing risks and improving productivity.